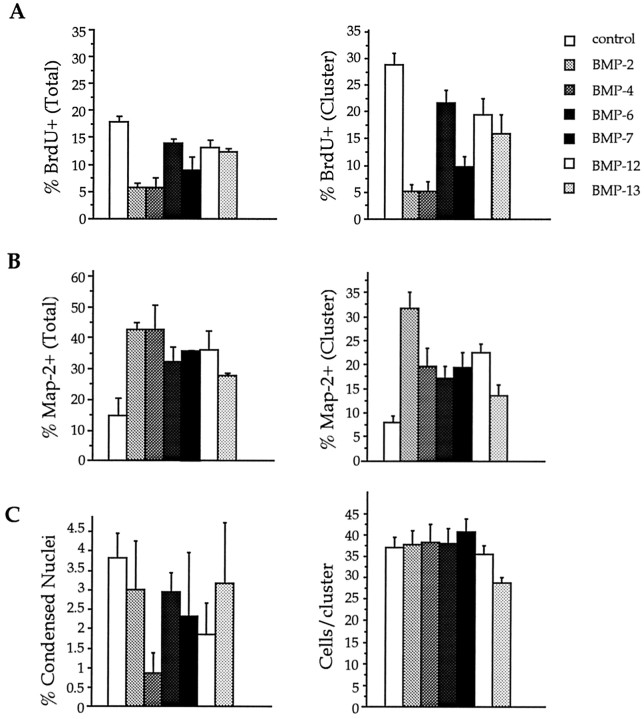
Fig. 2.
BMPs promote neuronal differentiation and inhibit BrdU incorporation in E12–E13 neocortical precursors.A, BMPs from three factor subgroups, the Dpp group (BMP-2 and BMP-4), the 60A group (BMP-6 and BMP-7), and the GDF group (BMP-12 and BMP-13) were applied to cell cultures at 30 ng/ml. These growth factors decrease BrdU incorporation after only 1 DIV. The effect was significant at p < 0.01 compared with control when expressed as the BrdU incorporation percentage in the total population (left; ANOVA; n = 7). It also shows a significant difference when expressed as the BrdU percentage per cluster (right; p < 0.001; n = 7). BMP-2 and BMP-4 led to the greatest decrease in the percentage of BrdU-incorporating cells. BMP-7 had effects comparable to those of BMP-2 and BMP-4. B, BMPs (30 ng/ml) promote neuronal differentiation as measured by the percentage of total cells that express MAP-2 (left;p < 0.01; ANOVA; n = 7) or by the MAP-2 percentage per cluster (right;p < 0.001; n = 7). BMP-2 and BMP-4 led to the greatest increase in MAP-2–immunopositive cells.C, The percentage of condensed nuclei in the total cell population (left) and the survival of cells per cluster (right) show no statistical difference between control and BMP-treated cell cultures.