Fig. 8.
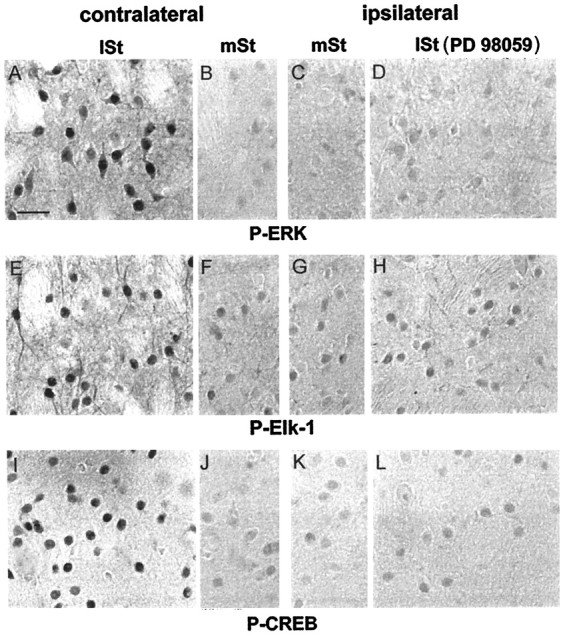
ERK proteins dually control Elk-1 and CREB hyperphosphorylation. Brains of PD 98059-injected rats, stimulated for 15 min, were processed for P-ERK (A–D), P-Elk-1 (E–H), and P-CREB (I–L) immunoreactivity. The injection of PD 98059 completely prevented ERK activation in the lateral striatum (lSt) ipsilaterally (D), but not contralaterally (A), to the inhibitor injection site. In the medial striatum (mSt) P-ERK immunoreactivity remained low in both sites (B, C). On sections adjacent to those used below, Elk-1 and CREB hyperphosphorylation were impaired in the lSt ipsilaterally (H andL, respectively), but not contralaterally (E and I, respectively), to the PD 98059 injection. The constitutive P-Elk-1 (F,G) and P-CREB (J,K) immunostaining remained low in both medial striata and was comparable to the immunolabeling observed inlSt ipsilaterally to the PD 98059 injection (H, L). Scale bar, 1 cm = 25 μm.
