Fig. 7.
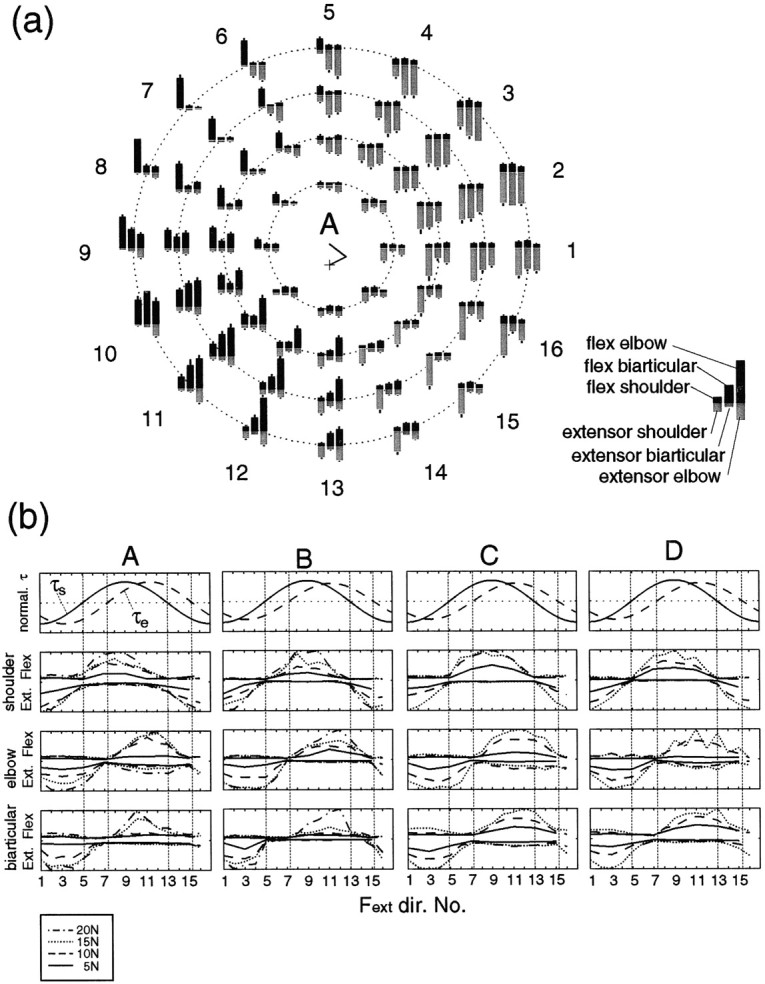
a, The magnitudes of rectified and averaged surface electromyograms (EMG level) from six muscles (shoulder monoarticular flexor and extensor muscles, biarticular flexor and extensor muscles, and elbow monoarticular flexor and extensor muscles) during force regulation tasks in 16 directions without cocontraction (instructed) at the proximal hand position (subject A). The magnitudes of EMG were normalized by the maximum EMG value for each muscle within these tasks. The EMG results of flexor muscles are depicted as theblack bars in the top portion of each graph, and the EMG results of extensor muscles are depicted as thegray bars in the bottom portion of each graph. Error bar on each bar graphrepresents SD of 24 trials of the corresponding EMG level. The manner of graph arrangement is the same as in Figure 6a.b, Changes in joint torque and EMG levels of six muscles for all four subjects according to force direction. The top row shows the normalized torque. The second rowshows the normalized EMG levels of the shoulder monoarticular flexor (upper side) and extensor (lower side) muscles. Thethird and fourth rows show the normalized EMG levels of the elbow monoarticular and the biarticular muscles, respectively, in the same manner as the second row.
