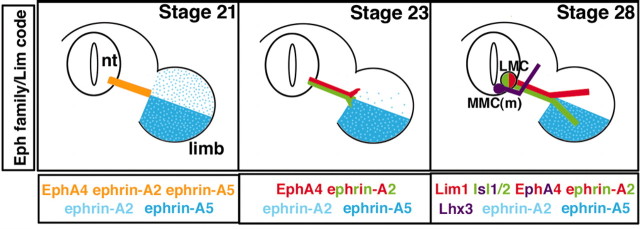
Figure 1.
The expression of Eph family members and the Lim code during the development of motor axon projections to target muscle. All diagrams illustrate expression patterns at the level of the crural plexus in the hindlimb. Left, All motor axons express EphA4, ephrin-A2, and ephrin-A5 (gold) when they reach the base of the hindlimb at stage 21. Ephrin-A2 is diffusely expressed across the hindlimb mesoderm, whereas ephrin-A5 is restricted to the ventral hindlimb. Middle, As motor axons initiate sorting in the plexus at stage 23, EphA4 is segregated to the forming dorsal nerve trunk (red) and presumably downregulated on the forming ventral nerve trunk. Ephrin-A5 protein is absent on motor axons whereas ephrin-A2 remains on all motor axons (red, green). Right, When the adult pattern of axon projections have formed, motor neurons in the LMC(l) (green) express Lim1, EphA4, and ephrin-A2 and enter the dorsal hindlimb, which lacks ephrins. Motor neurons in the LMC(m) (red) project to the ventral hindlimb, which is rich in ephrins (blue) and express Isl1/2 and ephrin-A2, but not EphA4. MMC(m) neurons (purple) project to epaxial muscle and express Lhx3, Isl1/2, and EphA4 (this study).