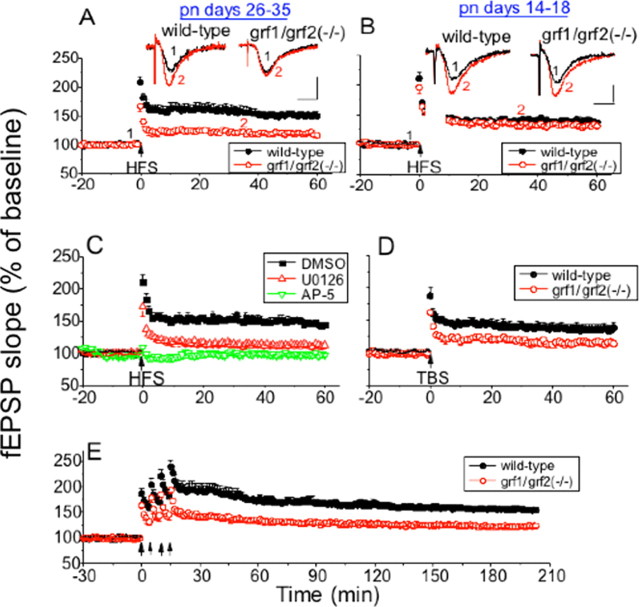
Figure 1.
LTP is impaired in the Schaffer collateral→CA1 pathway of hippocampal slices from postpubescent (P26–P35), but not in prepubescent (P14–P18) double Ras-GRF knock-out mice. HFS (two 100 Hz trains) was used to induce LTP in hippocampal slices from P26–P35 (A) and P14–P18 (B) wild-type and double Ras-GRF [grf1/grf2(−/−)] mice. Both groups received two trains of 100 Hz (1 s, 20 s delay) indicated by the arrow. The recorded fEPSP slope is expressed as a percentage of baseline ± SEM, and data were pooled from each group [closed circles, wild-type slices (A, n = 15; B, n = 12); open circles, grf1/grf2(−/−) slices (A, n = 13; B, n = 10)]. Insets, Representative fEPSPs recorded before (1) and after (2) HFS in wild-type and grf1/grf2(−/−) slices. Calibration: horizontal, 10 ms; vertical, 1 mV. C, Hippocampal brain slices were pretreated with buffer containing DMSO (closed boxes; n = 7), the MEK inhibitor U0126 (20 μm; upward triangle; n = 7), or the NMDAR inhibitor d-AP-5 (100 μm; downward triangle; n = 4) before HFS stimulation. Data are expressed as in A, B. D, TBS was used in mature wild-type (closed circles; n = 8) and ras-grf1/grf2(−/−) slices (open circles; n = 7); the recorded data are expressed as in A–C. E, Late-phase LTP was induced by four trains of 1 s, 100 Hz tetani (5 min delay) in mature wild-type (closed circles; n = 8) and grf1/grf2(−/−) slices (open circles; n = 8); the data are displayed as in A–C.