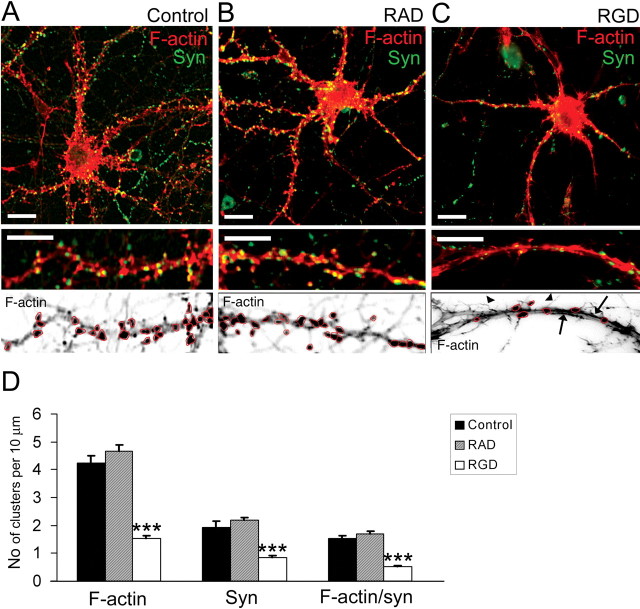
Figure 4.
RGD induced actin reorganization and synapse remodeling in 14 DIV hippocampal neurons. A–C, Confocal images of 14 DIV mouse hippocampal neurons untreated (A), or treated with 500 μm RAD-containing peptide (B) or with 500 μm RGD-containing peptide (C). Detection of polymerized F-actin with rhodamine-coupled phalloidin (red) and presynaptic boutons by synaptophysin immunostaining (green) is shown. Bottom panels show inverted fluorescent images of dendritic fragments with characteristic F-actin labeling for each group. Control untreated (A) or control RAD-treated (B) 14 DIV neurons demonstrated F-actin clusters in close proximity to synaptophysin-positive presynaptic boutons. RGD-treated (C) neurons showed a significant reduction in the number of F-actin puncta (circled), the appearance of hair-like extensions (arrowheads), and a decreased number of synaptophysin-positive terminals. Moreover, rope-like actin bundles were seen in the dendritic shaft of RGD-treated neurons (arrows). Scale bar: top panels, 10 μm; bottom panels, 5 μm. D, Quantitative analysis of the number of F-actin, synaptophysin, and actin/synaptophysin double-positive clusters per 10 μm of dendrite. RGD-treated neurons showed reduction in the number of F-actin clusters, synaptophysin-positive presynaptic boutons, and spiny synapses. Data represent the average number of clusters per 10 μm of dendrite. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 15 neurons per group). ***p < 0.001 with one-way ANOVA.