Figure 5.
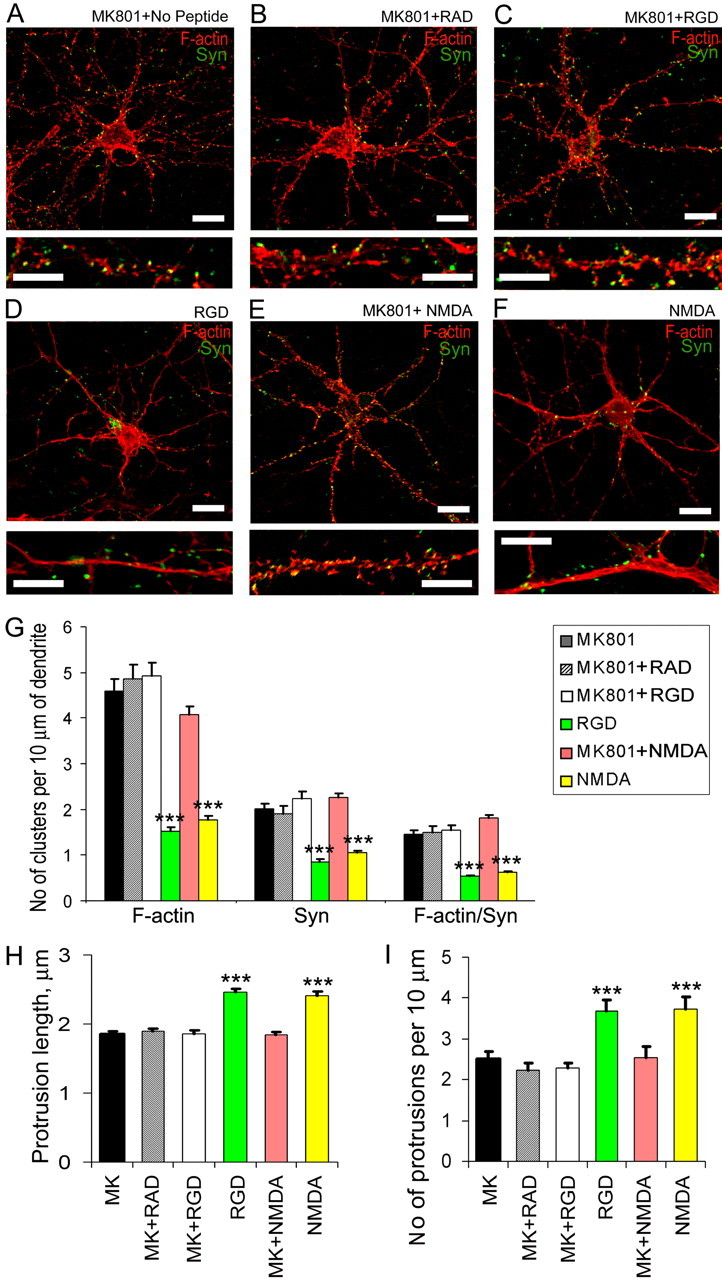
Blockade of NMDAR with MK801 prevented RGD-induced actin reorganization at synapses and dendritic spine remodeling. A–F, Confocal images of 14 DIV hippocampal neurons from cultures treated with MK801 (A), MK801 plus RAD (B), MK801 plus RGD (C), RGD (D), MK801 plus NMDA (E), or NMDA (F). Detection of polymerized F-actin with rhodamine-coupled phalloidin (red) and presynaptic boutons by synaptophysin immunostaining (green) is shown. NMDAR blockade with its antagonist MK-801 (10 μm) prevented both RGD-induced and NMDA-mediated actin rearrangements. Scale bar: top panels, 10 μm; bottom panels, 5 μm. G, Quantitative analysis of the number of F-actin, synaptophysin, and actin/synaptophysin double-positive clusters per 10 μm of dendrite. Treatment with MK801 blocked RGD-induced and NMDA-mediated reduction in the number of F-actin clusters, synaptophysin-positive presynaptic boutons, and spiny synapses. Data represent the average number of clusters per 10 μm of dendrite. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 10 neurons per group). ***p < 0.001 with one-way ANOVA. H, I, Quantification of dendritic protrusion length (H) and number (I) in 14 DIV GFP-labeled hippocampal neurons after treatment with MK801, MK801 plus RAD, MK801 plus RGD, RGD, MK801 plus NMDA, or NMDA. Treatment with MK801 blocked RGD-induced and NMDA-mediated dendritic spine elongation and new filopodia extension. Data represent the mean protrusion length (H) or average number of protrusions per 10 μm of dendrite (I). Error bars indicate SEM (n = 10 neurons per group). ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA.
