Figure 4.
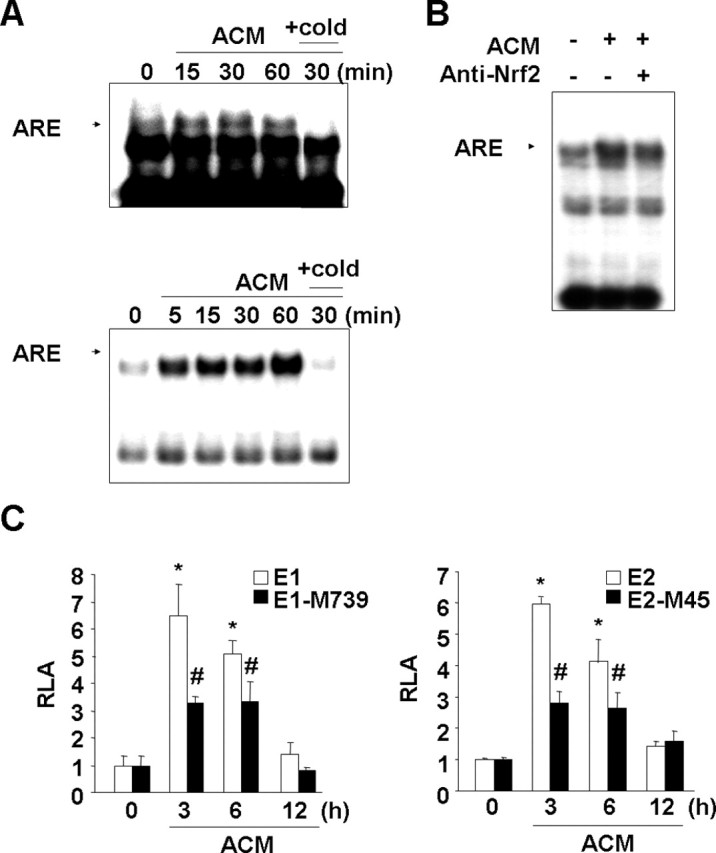
ACM induces ARE binding activity in nuclear extracts and enhances HO-1 promoter activity in an ARE-dependent manner. A, Primary microglia (top) and BV2 cells (bottom) were treated with ACM for the indicated times. Nuclear extracts were prepared, and the ARE-specific oligonucleotide–protein complexes were detected with an electrophoresis mobility shift assay. Addition of excess (X20) unlabeled oligonucleotide (cold) was used to determine specific binding of labeled oligonucleotides to the nuclear protein. B, For the supershift assay, nuclear extracts were prepared from BV2 cells treated with ACM for 30 min, mixed with 3 μg of Nrf2 antibody, and assayed for ARE-specific oligonucleotide–protein complexes as described in Materials and Methods. C, HO-1 promoter/luciferase fusion constructs, E1 and E2, and ARE site-mutated E1-M739 and E2-M45 constructs were transfected into BV2 cells. The transfected cells were treated with ACM for the indicated times and then assayed for luciferase activity as described in Materials and Methods. Values in C are mean ± SEM of three samples and represent relative luciferase activity (RLA). *p < 0.01 compared with the vector control. #p < 0.01 compared with the E1 or E2. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
