Figure 1.
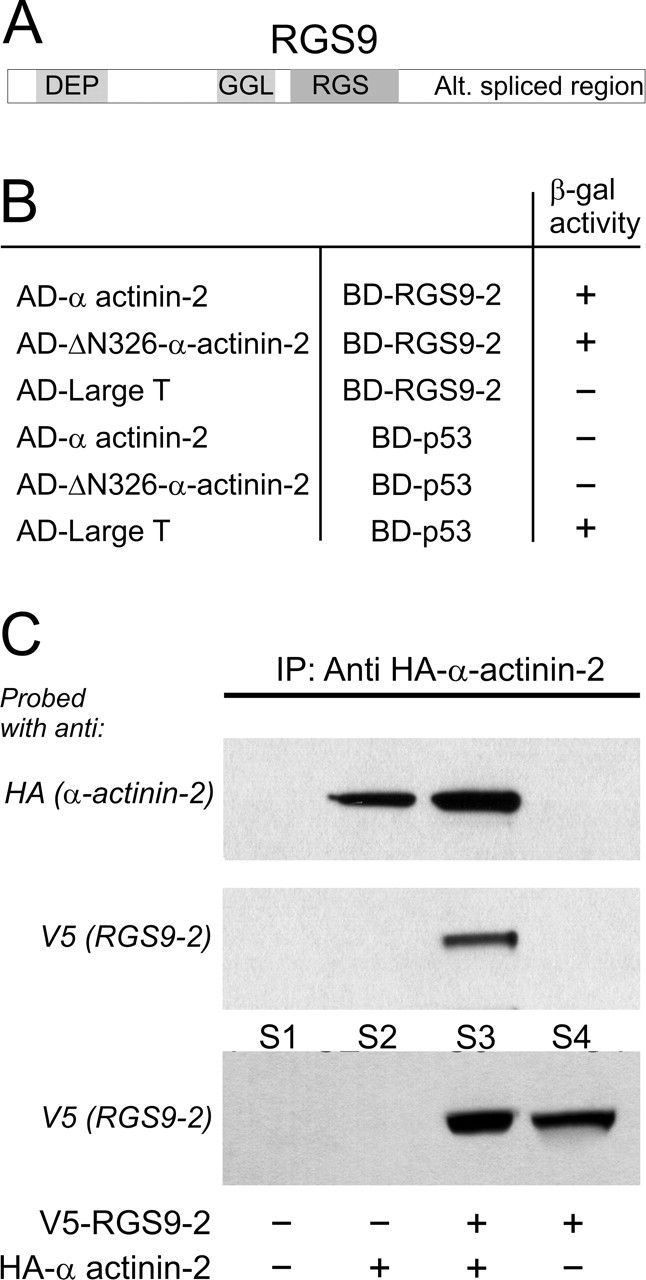
Brain-specific RGS9-2 binds the cytoskeletal protein α-actinin-2. A, Domain structure of RGS9: DEP domain, GGL domain, RGS domain, and a C terminus that is alternatively spliced. B, A human brain cDNA library was screened in a yeast two-hybrid assay using full-length RGS9-2 as bait. The initial screening identified a strong interaction of RGS9-2 with a truncated α-actinin-2 construct (designated as ΔN-326-α-actinin-2). This interaction was confirmed using full-length α-actinin-2. No interaction was seen between RGS9-2 and the large T antigen or between α-actinin-2 and p53 (negative controls), although the large T antigen interacted with p53 (positive control). C, RGS9-2 and α-actinin-2 physically interact when coexpressed in HEK-293 cells. Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-tagged α-actinin-2 and V5-tagged RGS9-2, either individually or in combination (1:1 ratio). Robust RGS9-2 expression was evident in the supernatant (S) from cells transfected with V5-tagged RGS9 or V5-tagged RGS9 plus HA-tagged α-actinin-2 (bottom panel, S4 and S3, respectively). HA-tagged α-actinin-2 was immunoprecipitated only from cells transfected with HA-tagged α-actinin-2 or HA-tagged α-actinin-2 plus V5-tagged RGS9-2 (top panel, lanes 2 and 3, respectively) but not from cells transfected solely with V5-tagged RGS9-2 (lane 4) or mock transfected (lane 1). Immunoprecipitation of HA-tagged α-actinin-2 coimmunoprecipitated V5-tagged RGS9-2 from cells cotransfected with V5-tagged RGS9-2 and HA-tagged α-actinin-2 (middle panel, lane 3) but not from singly- or mock-transfected cells (middle panel, lanes 1, 2, and 4). This experiment was replicated four times with comparable results.
