Figure 4.
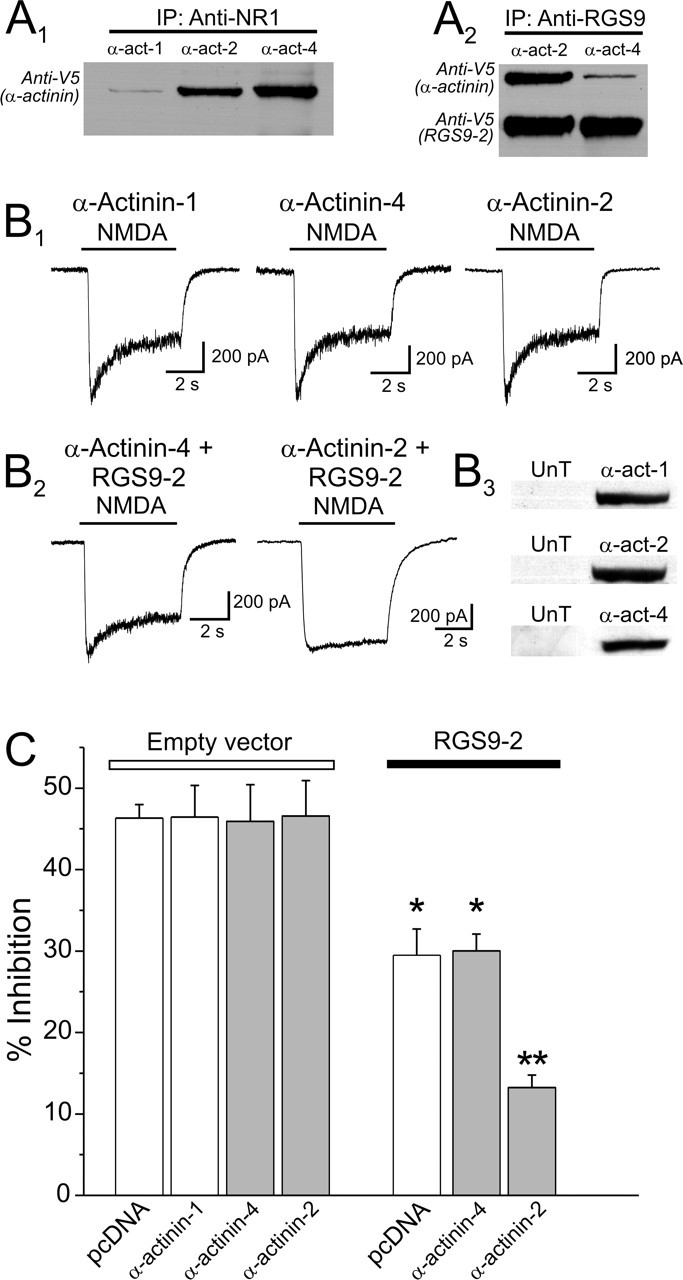
Effect of different α-actinin isoforms on the ability of RGS9-2 to modulate CDI. A1, α-Actinin-4 or α-actinin-2 interact with NR1. Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding NR1, NR2A, RGS9-2, and V5-tagged α-actinin-1, -2, or -4. NMDARs were immunoprecipitated using an anti-NR1 antibody, and an anti-V5 antibody was used to probe for the coimmunoprecipitation of each of the α-actinin isoforms. Immunoprecipitation of NR1 effectively coimmunoprecipitated α-actinin-4 and α-actinin-2 but only a trace amount of α-actinin-1. A2, In these same cells, immunoprecipitation of RGS9-2 preferentially coimmunoprecipitated α-actinin-2 vis-à-vis α-actinin-4. B1, Overexpression of α-actinin-1, α-actinin-4, or α-actinin-2 does not affect the expression of CDI in HEK-293 cells. B2, Expression of α-actinin-4 had no detectable effect on the ability of RGS9-2 to modulate CDI. In contrast, expression of α-actinin-2 markedly facilitated the ability of RGS9-2 to modulate NMDAR CDI. B3, Western blot confirming the overexpression of the different α-actinin isoforms in the HEK-293 cells used for these experiments. An anti-α-actinin-2 antibody and an anti-pan α-actinin antibody were used for this experiment. Endogenous α-actinins were below the level of detection for the probing conditions. C, Plot summarizing the results of this experiment. pcDNA3, 23 cells; α-actinin-1, 17 cells; α-actinin-4, 13 cells; α-actinin-2, 8 cells; RGS9-2, 15 cells; RGS9-2 plus α-actinin-1, 14 cells; RGS9-2 plus α-actinin-4, 16 cells; RGS9-2 plus α-actinin-2, 20 cells. *p < 0.01 against the respective control group; **p < 0.01 against α-actinin-2 alone and also against RGS9, RGS9-2 plus α-actinin-1, or RGS9-2 plus α-actinin-4 (ANOVA, followed by protected t test). UnT indicates mock-transfected cells. Error bars indicate SE.
