Fig. 2.
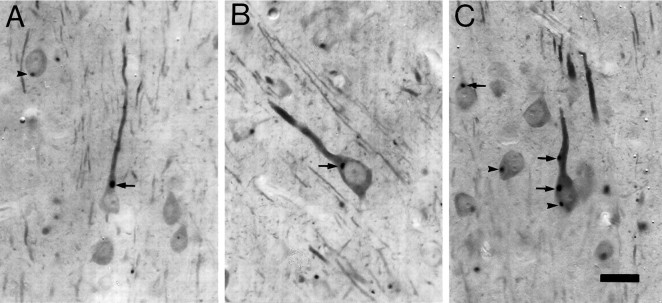
Cat-307 identifies a cytoplasmic structure in neurons that is often located near a major dendrite.A–C, Three layer V neurons containing Cat-307 immunoreactive botrysomes. In 50-μm-thick sections, Cat-307 immunoreactive profiles are observed in the cytoplasm of neurons and are most often found within, or just below, the apical dendrites of pyramidal cells. A, Two botrysomes, one located at the base of the large apical dendrite of a layer V pyramidal neuron (arrow) and the other in the basal portion of a neuron (arrowhead). The apical dendrite of the pyramidal neuron (arrow) contains a small botrysome farther from the cell body. B, A layer V pyramidal cell with a botrysome located just below the apical dendrite and very close to the nucleus.C, A large layer V pyramidal cell containing three immunoreactive botrysomes within its cell body and apical dendrite. Two of the botrysomes are associated with the apical dendrite (arrows), one located within and the other at the base of the dendrite. The third is located in the basal portion of the cell body (arrowhead). Such a basally located botrysome would have been classified as not associated with a dendrite; however, the basal dendrites of the cell are out of the plane of section, and this botrysome may also be at the base of a dendrite. The largest botrysomes are seen in layer V neurons, where they can reach a diameter of 4 μm. The diameter of botrysomes varies; even within a single cell, botrysome size does not correlate with neuronal size, although the smallest botrysomes are usually found within dendrites. Scale bar, 20 μm.