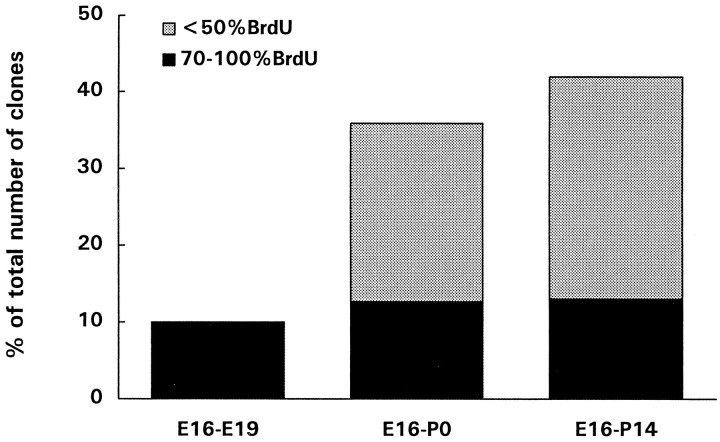
Fig. 5.
Histogram showing the percentages of isolated β-gal+ cells over the total number of clusters and pairs at different ages, after the injection of retrovirus and BrdU at E16, and the proportion of these cells that displayed high levels of BrdU immunoreactivity (dark bars). Isolated β-gal+ cells were studied in E19 rat embryos (3 d after injections), in newborn rats, and in 2-week-old rats. Less than 10% of the clones found at E19 were composed of a single cell, all of which displayed high levels of BrdU immunoreactivity. At later times after the injections, isolated β-gal+ cells increased in number, possibly as a result of tangential migration and/or death of clonal relatives. However, the number of single-cell clones (isolated cells with high levels of BrdU immunoreactivity) remained constant and represented ∼10% of all clusters at any age examined. The results obtained are pooled from at least five animals for each age group.