Figure 2.
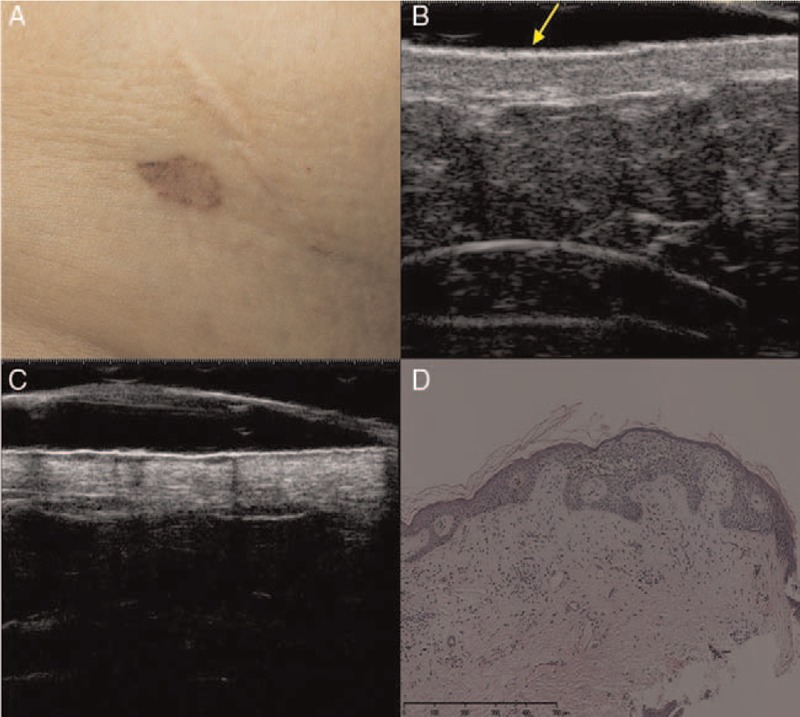
Superficial basal cell carcinoma. Clinical (A), ultrasonographic (B, C), and histological (D) images of superficial basal cell carcinoma (low-risk sub-type). (A) The clinical image shows an irregularly pigmented patch on the right abdomen. (B) A 20-MHz ultrasound examination revealed an ill-defined epidermal and upper dermal ribbon-like thickening with a slightly hypo-echoic upper dermis (arrow). (C) A 50-MHz ultrasound examination showed a well-defined, epidermal and upper dermal thickening with epidermal undulation and a homogeneous hypo-echoic ribbon-like upper dermal zone. No signs of hyper-echoic spots internal or posterior echoes were detected. (D) The lesion was confirmed histopathologically to be superficial basal cell carcinoma (hematoxylin-eosin staining, original magnification ×200).
