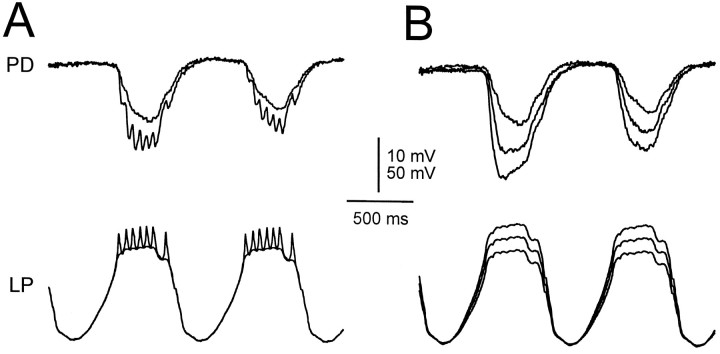
Fig. 12.
Effect of simulated spike-mediated IPSPs. A, IPSPs in response to 1 Hz LP waveforms with the spikes filtered out (smooth trace) and with the spikes not filtered (jagged trace). The nonfiltered waveform elicited an IPSP that was larger in amplitude than that of the filtered waveform and was jagged. The jaggedness corresponded one-to-one to IPSPs elicited by the simulated spikes. The jagged trace was also faster to rise. Vertical bar, 10 mV (PD) and 50 mV (LP). B, The gIPSPs in response to the filtered LP waveforms from A compared with the response to the same waveform (bottom LP trace), amplified to the average of the nonfiltered waveform in A (middle LP trace), and amplified to the outer envelope(maximum) of the nonfiltered waveform in A (top LP trace). The larger waveforms elicited gIPSPs that were larger in amplitude and faster to rise. The large amplitude and fast rise of the response to the nonfiltered waveform inA was accounted for by the response to the average of that waveform (middle LP trace). The membrane potential of the PD neuron was −42 mV.