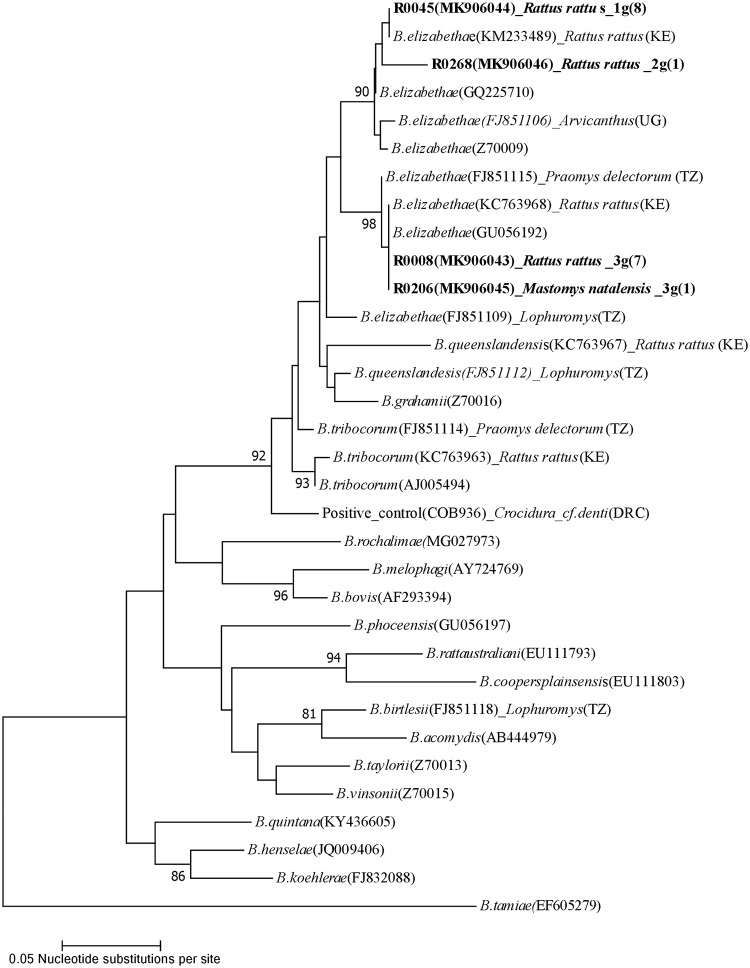
Fig 3. Phylogenetic tree showing the relatedness of the Bartonella gltA gene sequences (283bp fragments) derived from 17 spleen tissue samples from rodents (16 R. rattus and 1 Mastomys natalensis) trapped in northern Tanzania.
A single representative sample sequence is included for each genotype identified in this study, with the exception of genotype 3g to illustrate the identical sequences obtained from R. rattus and M. natalensis. Sequences from this study are labelled with unique identifiers, with prefix “R” followed by sample identifier numbers, Genbank accession number, the rodent or flea host species, the genotype code and the number of samples yielding each genotype (in parentheses). Reference Bartonella sequences from rodents trapped elsewhere in East Africa obtained from GenBank are indicated by GenBank accession numbers in parentheses, rodent species and country code (Kenya (KE) [22], Uganda (UG) [26] Tanzania (TZ) [25], Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) [25]). The sequence obtained for the known Bartonella positive control sample provided by a colleague from a previous study is included and indicated with a unique identification number (COB936) [24].