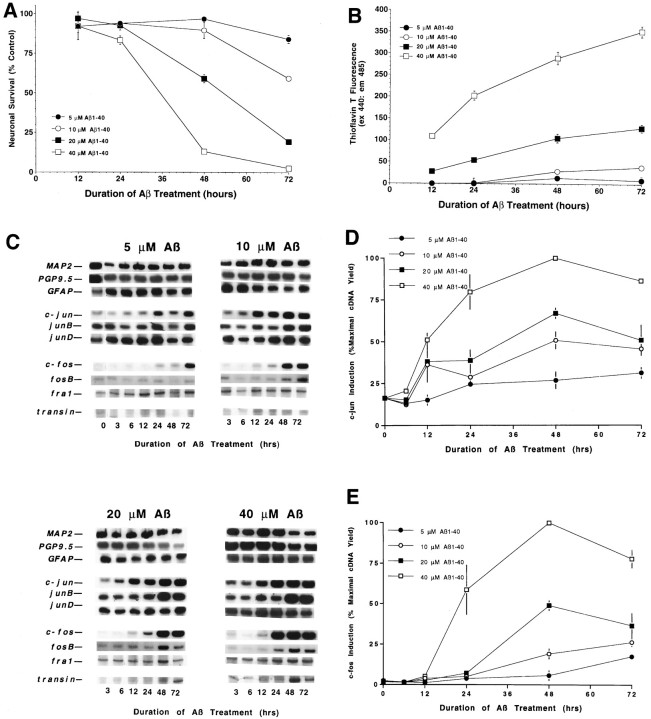
Fig. 4.
Gene induction and death are dependent on Aβ concentration. Cortical neuronal cultures were treated with Aβ1–40 (lot ZM605) for the indicated concentrations and times. Viability was determined by measuring alamarBlue reduction (A) and Aβ aggregation assessed by changes in ThT fluorescence (B). Changes in gene expression were assessed by RT-PCR (C), with quantification for c-jun (D) andc-fos (E). Values for the alamarBlue and ThT assays are expressed as mean ± SD (error bars) from triplicate wells, whereas those for c-jun andc-fos inductions are the mean ± SE (error bars) from triplicate determinations. The induction of c-jun,junB, c-fos, fosB,transin, and death shows a strong dependence on Aβ concentration and aggregation. The induction of c-junwas significant (p < 0.05) for 5 μm Aβ at the 48 and 72 hr time points and at every time point after 6 hr for the higher Aβ concentrations. The induction ofc-fos was significant at 72 hr for 5 μmAβ, at 48 and 72 hr for 10 and 20 μm Aβ, and at 24, 48, and 72 hr for 40 μm Aβ [ANOVA comparison of Aβ-treated vs control samples (n = 3), withpost hoc Fisher PLSD test].