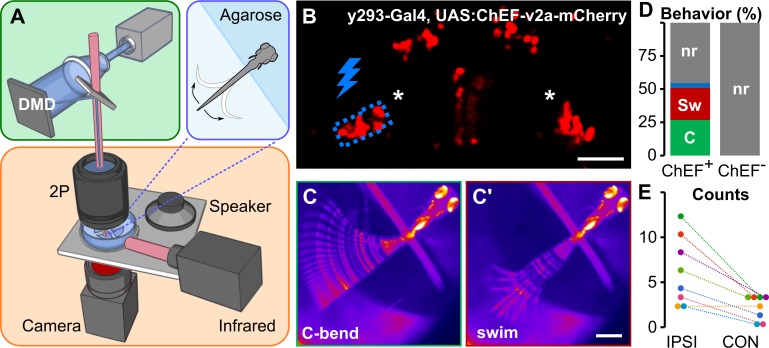
Fig 3. Optogenetic prepontine neuron stimulation elicits C-start behavior.
(A) Schematic of optogenetic stimulation and two-photon calcium imaging: a DMD was used to spatially restrict 460-nm LED excitation (green box) within the brain of head-embedded larvae (blue box) mounted on a stage with a speaker for acoustic/vibratory stimulation, an infrared light source for tail illumination, and a high-speed camera for behavioral readout (orange box). (B) Two-photon optical section of mCherry expression in y293-Gal4, UAS:ChEF-2a-mCherry larva with the area around one prepontine cluster (asterisks) stimulated by the DMD outlined in blue. Scale bar 40 μm. (C) C-start and swim-like (C') behaviors elicited by unilateral optogenetic stimulation of prepontine neurons in y293-Gal4, UAS:ChEF-positive larvae. Scale bars 500 μm. (D) Percent of behaviors elicited by illumination of larvae expressing ChEF (ChEF+; 229 trials, n = 8 larvae) and nonexpressing sibling controls (ChEF−; 63 trials, n = 7 larvae). C-start-like responses (“C,” green), swim-like bouts (“Sw,” red), other responses (blue), nr (gray). (E) Number of C-start responses made ipsilateral (“IPSI”) and contralateral (“CON”) to the side of optogenetic stimulation, color-coded for each of the 8 larvae tested. χ2 = 15.25, *p < 0.001. Underlying numerical data are included in S1 Data. DMD, digital mirror device; LED, light-emitting diode; mCherry, monomeric Cherry; nr, no response.