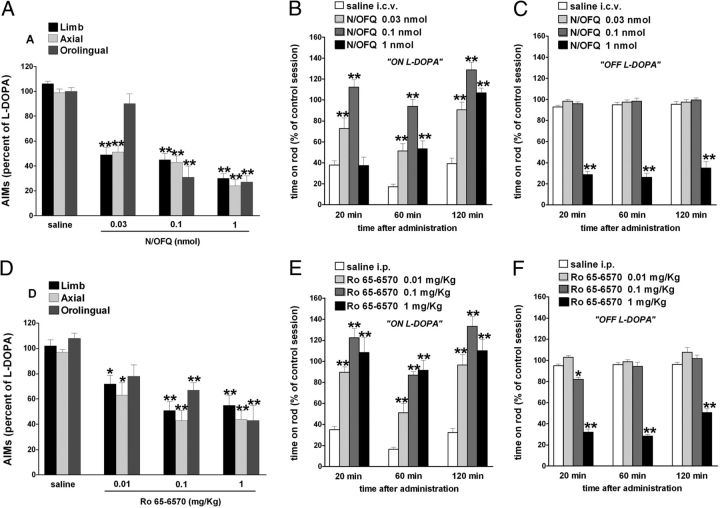
Figure 3.
NOP receptor agonists attenuated LID. Effect of N/OFQ (0.03–1 nmol, i.c.v.) and Ro 65–6570 (0.01–1 mg/kg, i.p.) on ALO AIMs induced by l-DOPA (6 mg/kg plus benserazide 15 mg/kg, i.p.). N/OFQ (A) or Ro 65–6570 (D), given 5 and 30 min before l-DOPA, respectively, attenuated the severity of dyskinesias in a dose-related fashion. N/OFQ and Ro 65–6570 improved rotarod performance ON l-DOPA (B, E) but worsened it OFF l-DOPA (C, F). Data are expressed as percentage of the l-DOPA effect measured in the same animal in the last training session, and represent the mean ± SEM of 10 determinations. Statistical analysis was performed by conventional (A, D) or RM (B, C, E, F) one-way ANOVA followed by the Newman–Keuls test for multiple comparisons. A, Significant effect of treatment (F(11,153) = 24.78, p < 0.0001). B, Significant effect of treatment (F(3,114) = 77.29, p < 0.0001), time (F(2,114) = 35.08, p < 0.0001), and time × treatment interaction (F(6,114) = 5.42, p < 0.0001). C, Significant effect of treatment (F(3,114) = 400.64, p < 0.0001), but not time (F(2,114) = 1.21, p = 0.30) or time × treatment interaction (F(6,114) = 0.64, p = 0.70). D, Significant effect of treatment (F(11,147) = 11.27, p < 0.0001). E, Significant effect of treatment (F(3,114) = 68.86, p < 0.0001) and time (F(2,114) = 18.24, p < 0.0001) but not time × treatment interaction (F(6,114) = 1.10, p = 0.36). F, Significant effect of treatment (F(3,114) = 387.52, p < 0.0001), time (F(2,114) = 20.66, p < 0.0001), and time × treatment interaction (F(6,114) = 5.39, p < 0.0001). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, significantly different from saline.