Figure 1.
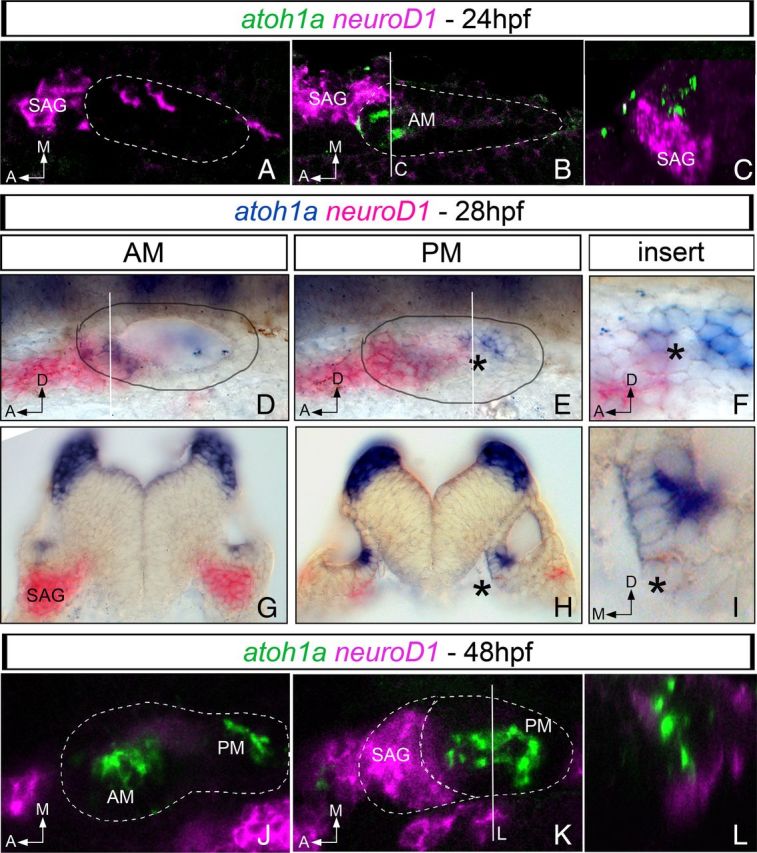
Expression of proneural genes for neurons and hair cells overlaps in the posteromedial domain of the otic vesicle. Whole-mount fluorescent (A–C, J–L) or chromogenic (D–I) double in situ hybridization for atoh1a (green/blue) and neuroD1 (magenta/pink) in 24 hpf (A–C), 28 hpf (D–I), and 48 hpf (J–L) zebrafish embryos. neuroD1 and atoh1a display non-overlapping regions of expression in the anterior aspect of the otic vesicle at 24 hpf: A, ventral confocal plane showing expression of neuroD1 in the most ventral aspect of the otic epithelium and in the SAG; B, more dorsal confocal plane showing expression of neuroD1 in the SAG and atoh1a in the otic epithelium; and C, yz confocal cross-section of B (white line) showing that neuroD1 and atoh1a are indeed expressed in neighboring cells. In 28 hpf embryos (D–I), neuroD1 and atoh1a display exclusive regions of expression in the anterior aspect of the otic vesicle and in the SAG (D, transverse section in G). Note the overlapping domain of gene expression in the posteromedial domain of the otic epithelium (black asterisk in E and in the corresponding transverse section in H). F and I are inserts of E and H, respectively. At 48 hpf (J–L), neuroD1 expression is mainly restricted to the SAG and atoh1a to the AM and PM (J, K). L, yz confocal cross-section of K (white line) showing that atoh1a and neuroD1 expression does not overlap. White dotted lines and black circles indicate the contour of the otic vesicle. Dorsal (A,B and J,K), and lateral views (D–F) with anterior to the left. G–I, Transverse sections. A, Anterior; D, dorsal; M, medial.
