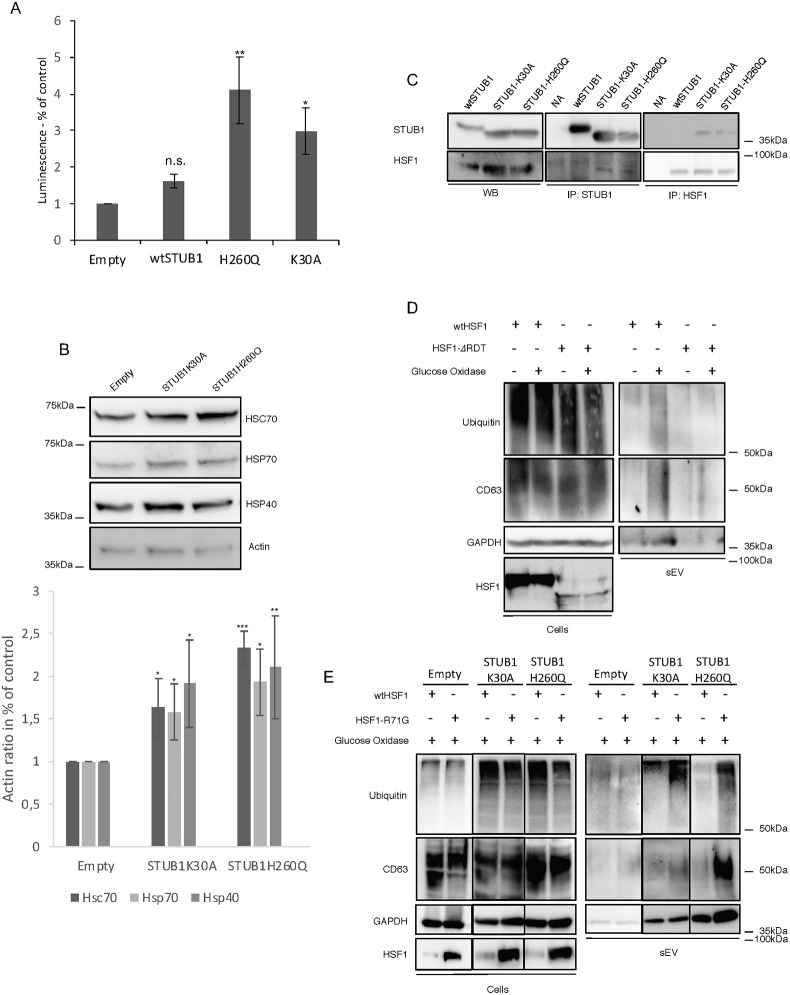
Fig 8. Expression of STUB1-DN increases HSF1 activity.
Activation of HSF1 inhibits GOx induced sEVs secretion. ARPE-19 cells were transduced using lentiviral particles containing vectors either for the expression of wtSTUB1, STUB1K30A and STUB1H260Q or with adenoviral particles containing shRNA against STUB1. Control cells were transduced with an empty vector. A) Cells were transfected with a plasmid for the expression of Luciferase under the control of an HSF1 promoter (HSE sequence). STUB1-DN mutants increase the expression of Luciferase. B) SDS-PAGE of extracts from cells expressing STUB1-DN incubated with antibodies raised against HSC70, HSP70, HSP40 and actin. Cells expressing the STUB1-DN mutant show an increase in the levels of molecular chaperones. C) Immunoprecipitation experiments using antibodies raised against V5 (wtSTUB1), myc (mutant STUB1) and HSF1 indicate that STUB1-DN mutants show increased interaction with HSF1, when compared with wtSTUB1. (D,E) Cells were transfected with plasmids for the expression of either wtHSF1, HSF1-ΔRDT or HSF1-R71G. Cells were further maintained in the presence or absence or 40 mU of GOx for 12h. SDS-PAGE of cell extracts or sEVs isolated by sequential centrifugation of cell culture media, were blotted with antibodies against ubiquitin, CD63, GAPDH or HSF1. (D) Expression of a constitutively active HSF1 (HSF1-ΔRDT) leads to the inhibition of sEVs release in the presence of GOx. (E) Expression of a dominant negative HSF1 (HSF1-R71G) rescues sEVs release upon GOx incubation. All samples were analyzed under the same experimental conditions. The results represent the mean ±SD of N = 3 independent experiments (n.s. nonsignificant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).