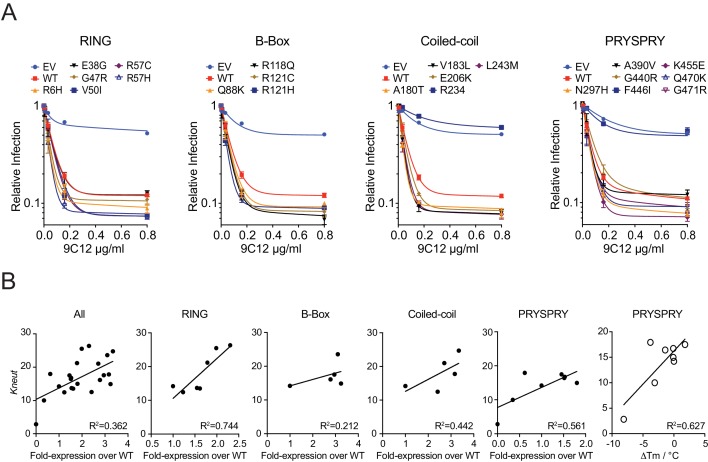
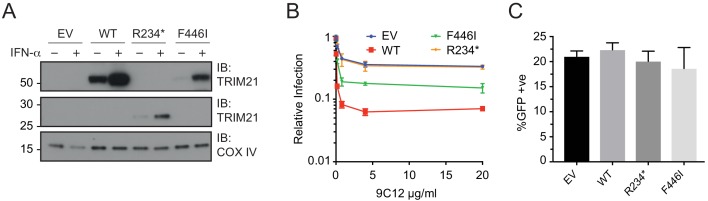
Figure 6. Viral neutralization by TRIM21 natural variants.
(A) Neutralization experiments were carried out in TRIM21 KO 293T cell lines stably reconstituted with TRIM21 variants expressed at endogenous levels. Each stable cell line was challenged with AdV5-GFP in the presence of the anti-hexon monoclonal antibody 9C12. The AdV5 vector contains a copy of the GFP gene and relative infection levels were quantified by flow cytometry and normalized to that of virus only condition. Data compiled from at least two independent experiments (mean ± SEM) and fitted to a one phase exponential decay. (B) Correlation of neutralization efficiency (Kneut, the exponential decay constant calculated from (A)), with cellular protein expression levels (from Figure 5) or thermostability (ΔTm) using linear regression analysis in GraphPad Prism7. Variants are grouped into their host domains. The R234* variant was excluded from correlative analysis. Data provided in Figure 6—source data 1.