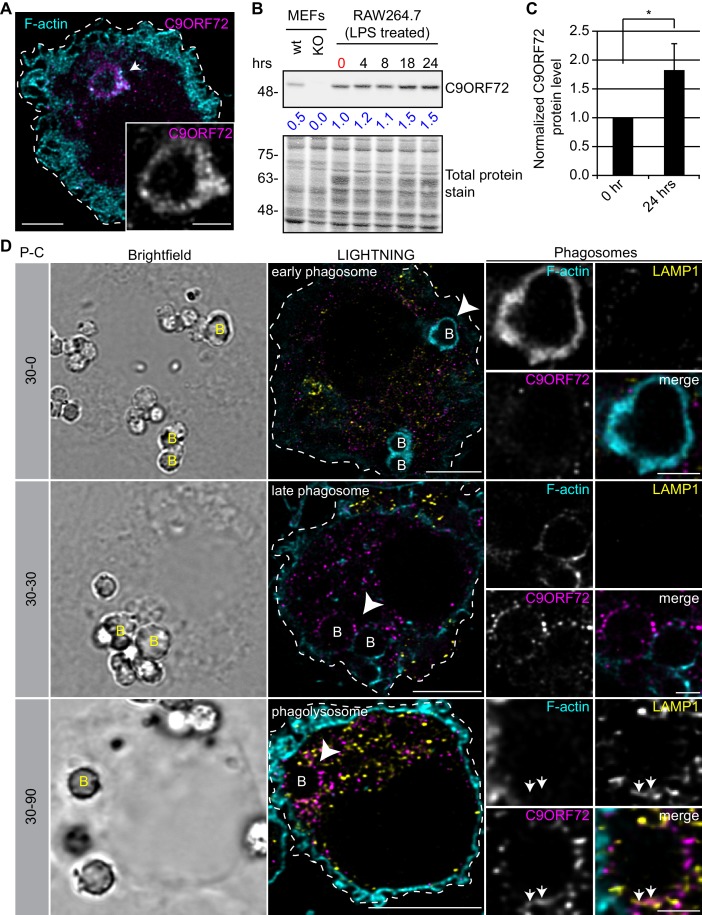
Figure 8. C9ORF72 localizes in part to late phagosomes and phagolysosomes.
(A) Immunofluorescence of C9ORF72 (GTX632041, magenta) and F-actin staining (cyan) in human MDMs. The inset is a higher magnification of the region indicated by the arrow and shows a grayscale image of C9ORF72. Cell is outlined with a white dashed line. Scale bar = 5 µm (full size) and 2 µm (inset). (B) Quantitative immunoblot of RAW264.7 cell lysates treated with 1 µg/ml LPS for the indicated time points. The total protein stained transfer is shown as loading control. C9ORF72 is detected using GTX634482. The C9ORF72 protein signal as a ratio to total protein was determined, normalized to RAW264.7 lysates at time 0 (red), and presented as fold change (blue numbers). C9ORF72 KO MEFs are included as a specificity control. (C) Quantification of C9ORF72 intensity from immunoblots performed as in (B) at 0 hr and 24 hr time points, presented as normalized values. Four individual experiments were quantified. *=p value<0.05 (D) Pulse-chase (P–C) experiments in LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells using phagocytosed beads. Beads were incubated for a 30 min pulse followed by a 0 min (30-0), 30 min (30-30) or 90 min (30-90) chase. Brightfield imaging reveals the phagocytosed beads. Staining of C9ORF72 (GTX632041; magenta), LAMP1 (yellow) and F-actin (cyan) were performed and imaged using confocal microscopy together with LIGHTNING image processing as described previously. Single focal plane images are shown. Insets are higher magnification views of the internalized beads indicated with arrowheads in the large images and show the merged channel together with grayscale images of F-actin, LAMP1 and C9ORF72. White arrows point toward C9ORF72 and LAMP1 co-localization. All images are the result of LIGHTNING applied to the confocal image. Cells are outlined with white dashed lines. Scale bar = 8 µm (full size) and 2 µm (inset).