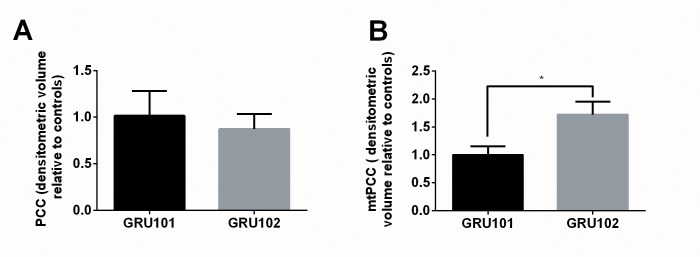
Figure 4. Evidence for ROS-related oxidative protein damage in GRU102.
(A) Densitometric analysis of protein carbonyl content (PCC) from whole lysate in young GRU101 and GRU102. (B) Densitometric analysis of mitochondrial protein carbonyl content (mtPCC) from whole lysate in young GRU101 and GRU102 (unpaired t-test, p<0.05, *; n = 3–7 repeats per condition, with approximately 1500 animals per repeat collected from independent cohorts).