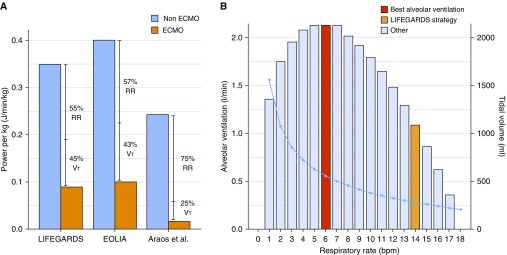
Figure 1.
(A) Mechanical power (MP) normalized per kilogram of body weight delivered during mechanical ventilation before and after onset of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in the LIFEGARDS (Ventilation Management of Patients with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and EOLIA (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) studies, as well as in the experimental study by Araos and colleagues (9), indicating a reduction (in percent) of MP attributed to the respiratory rate (RR) or the Vt. (B) We built a model for an MP (here we use the one delivered during ECMO in the LIFEGARDS study, 6.6 J/min) and a given dead space (200 ml) to establish the best combination of Vt and RR, with the aim of maximizing alveolar ventilation. Each column represents the alveolar ventilation at each different RR (left y-axis), and the light blue line represents the associated Vt (right y-axis). Positive end-expiratory pressure was kept constant (11 cm H2O) in this model, as were the airway resistances. bpm = breaths/min.