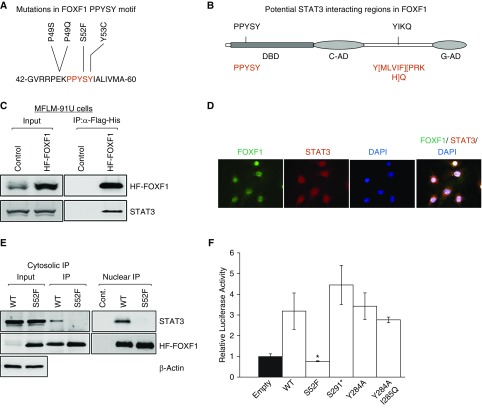
Figure 1.
S52F mutation disrupts FOXF1–STAT3 protein–protein interaction and decreases FOXF1 transcriptional activity. (A) Protein sequence shows a frequently mutated region, PPYSY (P49-Y53), located in DNA-binding domain of FOXF1. (B) Schematic diagram shows two potential SH2 domain-binding regions in FOXF1. Consensus STAT3-binding sequences are shown in red. (C) Immunoblots show STAT3 and FOXF1 proteins in immunoprecipitation fractions of MFLM-91 U cells after HF-FOXF1 purification. Cells stably expressing HF-Foxf1 were subjected to two-step affinity purification using anti-Flag Ab followed by nickel affinity columns. Vector alone–transduced cells were used as a control. (D) Immunofluorescent images show colocalization of FOXF1 and STAT3 proteins in nuclei of MFLM-91 U cells. Magnification ×400. (E) Immunoblots show that transfected S52F-FOXF1 protein does not interact with STAT3. Exogenous HF-FOXF1 mutant proteins were detected by α-Flag antibody. (F) S52F FOXF1 mutation inhibits transcriptional activity. Dual-luciferase assay was performed using 6× FOXF1-LUC reporter plasmid (n = 5 in each group). *P < 0.05. IP = immunoprecipitation; WT = wild type.