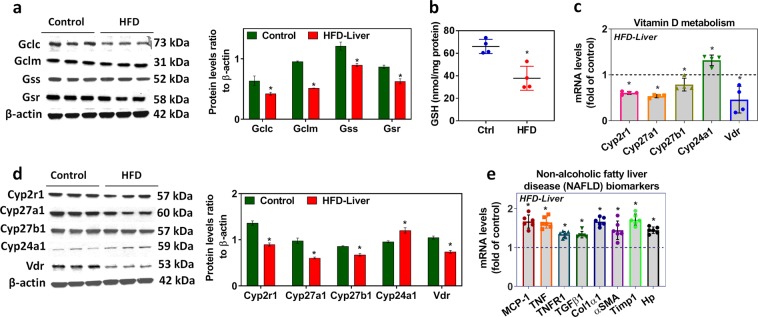
Figure 1.
Effect of HFD on liver GSH and vitamin D metabolism genes. (a) Representative Western blot analysis (GCLC, GCLM, GSS, and GSR) performed on total protein extracts (n = 3) from the livers of mice fed an HFD for 16 weeks compared with those from mice fed the control diet. The right panel represents the semi-quantitative analysis of the protein abundance ratio to β-actin. (b) Liver GSH levels. (c) RT-qPCR was performed to assess the levels of vitamin D metabolism gene mRNA as indicated (n = 4). (d) Representative Western blot analysis (CYP2R1, CYP27A1, CYP27B1, CYP24A1, and VDR) performed on total protein extracts (n = 3) from the livers of mice fed an HFD for 16 weeks compared with those from mice fed the control diet. The right panel represents the semi-quantitative analysis of the protein abundance ratio to β-actin. (e) RT-qPCR was performed to assess the mRNA levels of genes (MCP-1, TNF, TNFR1, TGFβ1, Colα1, αSMA, Timp1, and Hp) associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as indicated (n = 6). An unpaired Student’s t-test was used to compare the control group with the HFD group. *p ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.