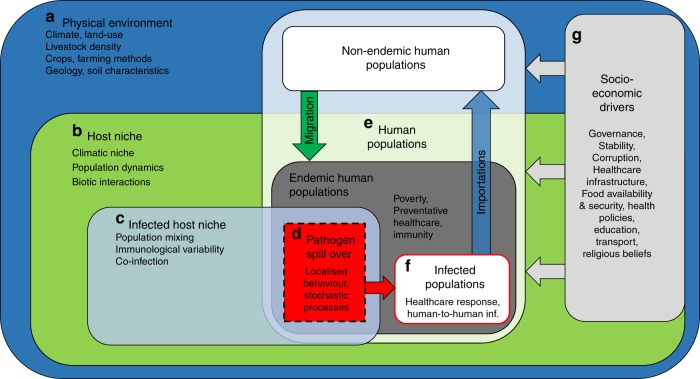
Fig. 1.
System-dynamics model of zoonotic disease transmission. Letters a–f indicate major system components, arrows showing links, and key sub-components in smaller font. Within the global physical environment (a), both the host niche (b) and infected host niche (c) are nested subsets, which all vary over a relatively slow time-scale. Endemic human populations are nested within the global human population (e), with human socio-economic factors (g) affecting all human populations. Spill-overs happen in the fast-moving spatial and temporal interface of these two nested systems (d), where both infected hosts, susceptible people and spill-over specific factors occur, resulting in infected human populations (f)