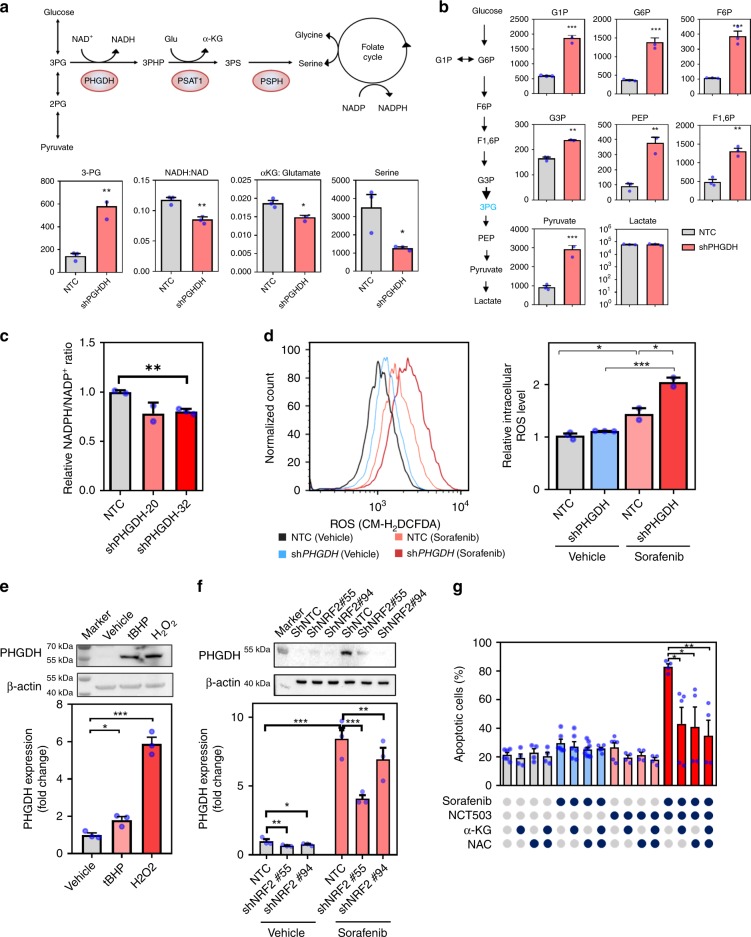
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of PHGDH impaired serine biosynthesis and induced oxidative stress. a Knockdown of PHGDH impaired serine synthesis pathway (SSP), leading to accumulation of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PG) and reduced production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+hydrogen (NADH), α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), and serine. b Glycolytic metabolites cannot be branched into SSP upon knockdown of PHGDH, causing the accumulation of most glycolytic metabolites glucose 1-phosphate (G1P), glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), fructose 6-phosphate (F6P), fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6P), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), and pyruvate (gray bar: non-target control; red bar: PHGDH knockdown clones). c Knockdown of PHGDH resulted in reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) production. d Sorafenib treatment augmented reactive oxygen species (ROS) level. Knockdown of PHGDH intensified the Sorafenib-induced oxidative stress in HCC cells (black line: non-target control treated with vehicle; light red line: non-target control treated with Sorafenib; blue line: PHGDH knockdown clones treated with vehicle; deep red line: PHGDH knockdown clones treated with Sorafenib). e H2O2 and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBHP) treatment at 20 and 200 μM for 24 h respectively induced PHGDH expression in HCC cells in both mRNA and protein level. f Knockdown of NRF2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2) alleviated Sorafenib-induced PHGDH up-regulation in HCC cells in both mRNA and protein level. g Treatment of α-KG at 4 mM and NAC at 5 mM for 48 h substantially inhibited Sorafenib (5 μM) and NCT-503(40 μM)-induced apoptosis in HCC cells. The error bar represents SEM. n = 3 biologically independent samples in panels a–f and 5 in panel g. Source data are provided as a Source Data file (Student's t-test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)