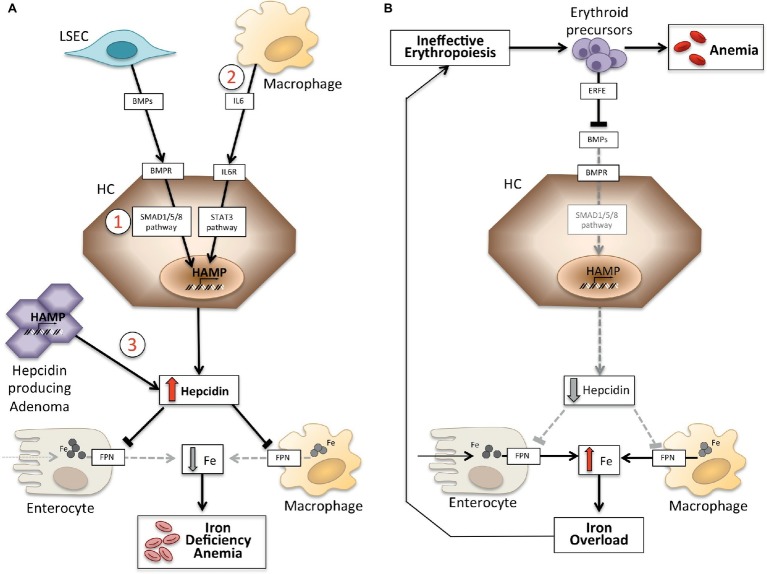
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of mechanisms of anemias with high (left panel) and low hepcidin (right panel). Panel (A). Molecular pathogenesis of anemia associated with high hepcidin levels. LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells producing bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs); BMPRs, BMP receptors; IL6, interleukin 6; HC, hepatocytes; HAMP, hepcidin gene. Fe, iron; FPN, ferroportin; 1, IRIDA; 2, Anemia of inflammation; 3, hepcidin producing adenoma. Panel (B). Molecular pathogenesis of hepcidin variation in anemias due to ineffective erythropoiesis. ERFE, erythroferrone sequestering BMPs. Other mechanisms inhibiting hepcidin in this type of anemia, as decrease of transferrin saturation and hypoxia, are not shown. See text for details.