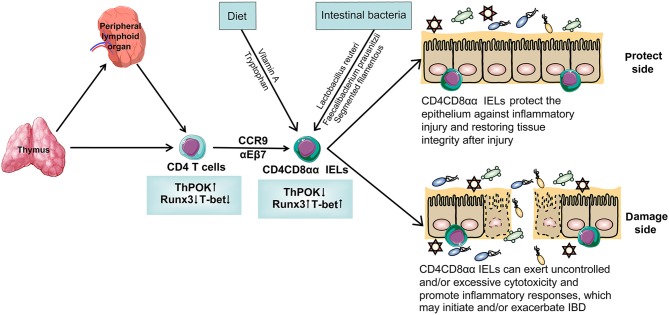
Figure 1.
The specific differentiation and development process of CD4CD8αα IELs. T cells originate from bone marrow and most of them develop in thymus while some of them develop in peripheral lymphoid organ. T cells differentiate into CD4 T cells with the help of transcription factors that are highly expressed ThPOK and lower-expression Runx3 and T-bet. With the help of the gut-homing markers CCR9 and α4β7, CD4 T cells migrate in the intestinal epithelium and are named CD4 IELs. These cells can acquire CD8αα on their cytomembrane and become a kind of special CD4 IELs, CD4CD8αα IELs. After interacting with intestinal bacteria and diet, CD4CD8αα IELs have a different function. On the one hand, CD4CD8αα IELs protect the epithelium against inflammatory injury, restoring tissue integrity after injury. On the other hand, it can exert uncontrolled and/or excessive cytotoxicity and promote inflammatory responses, which may initiate and/or exacerbate IBD.