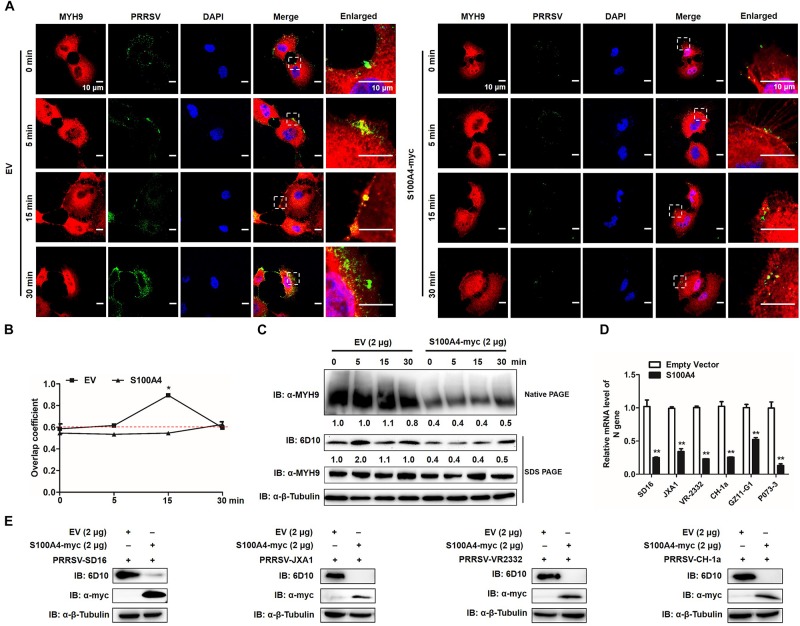
FIGURE 10.
GP5-ecto-1-PRA interaction-induced PRA aggregation correlates PRRSV internalization and sequential viral replication. (A) Co-localization in MARC-145 cells between PRRSV and MYH9. After exposure to PRRSV (MOI = 50) at 4°C for 2 h, MARC-145 cells expressing S100A4-myc or transfected with pCAGEN empty vector (EV) were transferred to 37°C for 0, 5, 15, and 30 min. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and subjected to immunofluorescence staining of MYH9 (Red) and PRRSV virions (Green). Images are representative one of three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Assessment of co-localization of MYH9 and PRRSV virions. The Mean of Manders’ overlap coefficient ± SD are representative of three individual enlarged pictures. ∗P < 0.05. (C) Cell treatment was performed as described in panel (A), followed by cell lysed and subjected to native-PAGE and Western blot using anti-MYH9 pAb and anti-PRRSV N mAb (6D10). Values are normalized to PRRSV-infected cells with EV-transfection that harvested at 0 min after temperature shift, and the fold of relative expression was indicated. (D) MARC-145 cells expressing S100A4-myc or transfected with pCAGEN empty vector (EV) were inoculated with indicated PRRSV strains at 50 MOI for 15 min. The RNA level of PRRSV-N expression was detected by qPCR. Values are normalized to EV-transfected cells with PRRSV infection. ∗∗P < 0.01. (E) Cell treatment was performed as described in panel (D) and then cells were washed with PBS buffer and cultured for 24 h. Virus replication was measured via Western blot using anti-PRRSV N mAb (6D10).