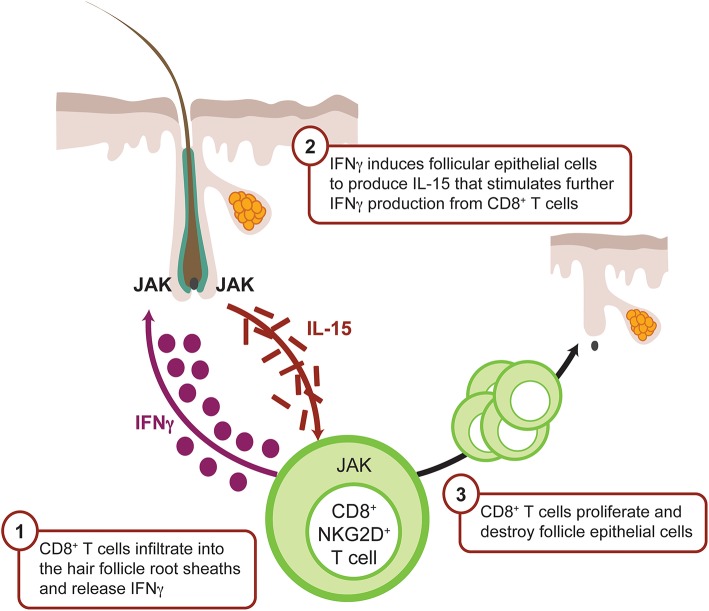
Figure 4.
IFNγ-driven inflammation in alopecia areata is JAK mediated. CD8+ T cells infiltrate the dermis, localize to the hair follicle bulb, and release IFNγ. IFNγ binds the IFN receptor on the surface of the follicular epithelial cell, which in turn signals via JAK1 and JAK2 to promote production of IL-15, a mediator of CD8+ T-cell activation. IL-15 binds IL-15 receptor on the CD8+ T cell surface, resulting in signaling via JAK1 and JAK3 to enhance the production of IFNγ and amplify the feedback loop. CD8+ T cells then attack the hair follicle, which causes hair loss. CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; IFN, interferon; JAK, Janus kinase.