Figure 4.
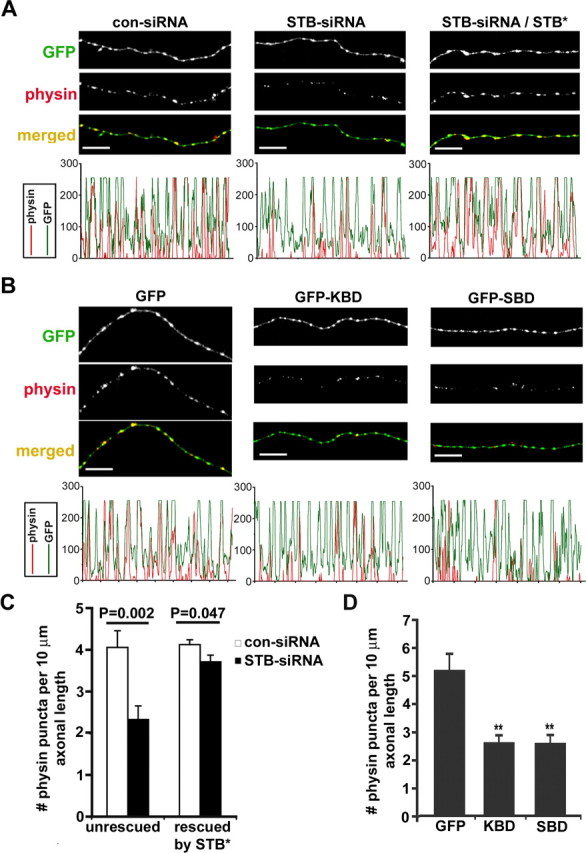
Syntabulin loss of function reduces the density of SV clusters within axons. A, Hippocampal neurons (DIV5) were transfected with either con-siRNA or STB-siRNA alone, or cotransfected with HA-STB*, followed by immunostaining for synaptophysin (physin; red) and MAP2 (blue) or HA-STB (data not shown) 4 d after transfection. The corresponding profiles within the MAP2-negative axonal segments show that STB-siRNA reduced the relative size and density of SV clusters and coexpression with HA-STB* rescued the phenotype. B, Representative axonal images of hippocampal neurons transfected at DIV7 with GFP, GFP-KBD, or GFP-SBD, followed by immunostaining at DIV9 for synaptophysin (red) and MAP2 (blue). Note that expression of the binding domain transgenes decreased both the size and density of SV clusters (red). C, D, The relative density of SV clusters within the axons expressing siRNA (C) or dominant-negative binding domain transgenes (D). Histograms represent the number of synaptophysin-labeled puncta per 10 μm axon length, and p values are calculated relative to that of neurons transfected with con-siRNA or con-siRNA/STB* (C) or GFP (D), respectively. The data were pooled from 13 neurons cultured on three separate coverslips. Total axon length measured was 1770.51 μm (con-siRNA), 1509.55 μm (STB-siRNA), 3392.95 μm (con-siRNA/STB*), 3317.92 μm (STB-siRNA/STB*), 1498.03 μm (GFP), 1809.38 μm (GFP-KBD), or 2803.15 μm (GFP-SBD). Error bars indicate SEM (**p < 0.001, Student's t test). Scale bars, 10 μm.
