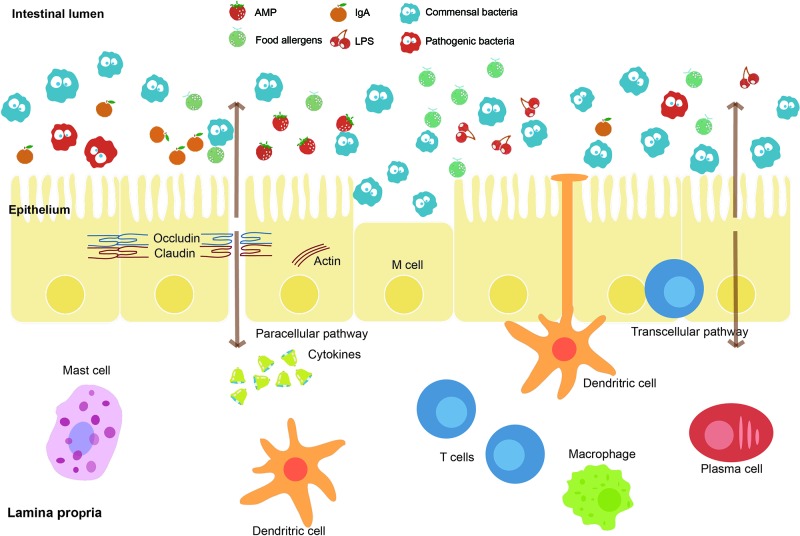
Figure 3.
Intestinal barrier and affecting factors. The intestinal barrier, as an essential barrier against harmful pathogens and substances in the intestine, mainly consists of the mucus layer, the epithelial layer, and the underlying lamina propria. The intestinal lumen contains antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), secreted IgA, and commensal bacteria, which prevent the colonization of pathogens. A mucus layer covers the intestinal surfaces as a physical barrier. The epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells sealed by tight junction proteins such as occludin and claudin inhibiting paracellular passage. M cells and intraepithelial lymphocytes are also contained in this layer. The lamina propria harbors lots of immune cells. Factors including food allergens, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and pathogenic bacteria such as EPEC effect on the intestinal barrier function.