Figure 1.
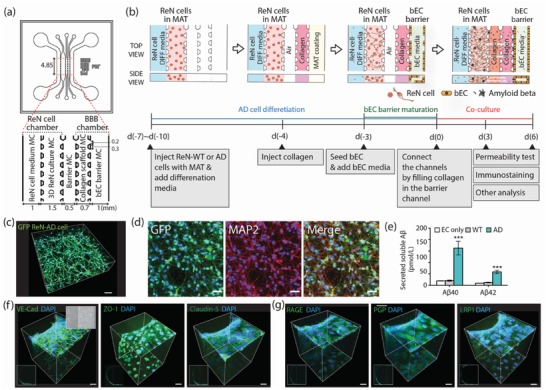
Schematic depiction of a WT/AD model and verification of function of 3D ReN culture and BBB integrity. a) The WT/AD model is composed of ReN‐WT/AD cell and BBB chambers with an intervening barrier microchannel (MC). The ReN cell chamber is composed of a ReN cell medium MC and 3D ReN culture MC, and the BBB chamber is composed of a collagen scaffold MC and bEC barrier MC. Numbers (mm) indicate the dimension of our microfluidic model. b) Sequential experimental protocol for WT/AD model development. The mixture of ReN‐WT or AD cells in Matrigel (MAT) was injected in 3D ReN culture MC, and ReN differentiation medium (DIFF medium) was added in ReN cell media MC. After 3 d, collagen type 1 (4.0 mg mL−1) was injected in the collagen scaffold MC, followed by MAT coating (1:50 in serum free media). Next day, bECs (hCMEC/D3) were seeded in the bEC barrier MC, and allowed to form a monolayer on the collagen scaffold and bottom and top of the MC. After monolayer formation, ReN cell and BBB chambers were connected by injecting collagen (2.0 mg mL−1) into the barrier MC. c) 3D‐differentiated GFP labeled ReN cells in 3D AD culture MC, and d) the representative image of 2‐week differentiated ReN‐AD cells that are stained with MAP2 (red) and an overlay image. Scale bars: 80 µm in (c) and 40 µm in (d). e) Levels of soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 detected in media from EC only, ReN‐WT, or ReN‐AD cells in the WT/AD models. f) Expression of junction protein (VE‐Cad) and tight‐junction proteins (ZO‐1 and Claudin‐5), and g) Aβ transporters (RAGE, PgP, and LRP‐1) in the bEC barrier of the AD model. The expression of tight junction proteins and Aβ transporters was confirmed by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bars: 40 µm. Data are mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis was by Student's t test.
