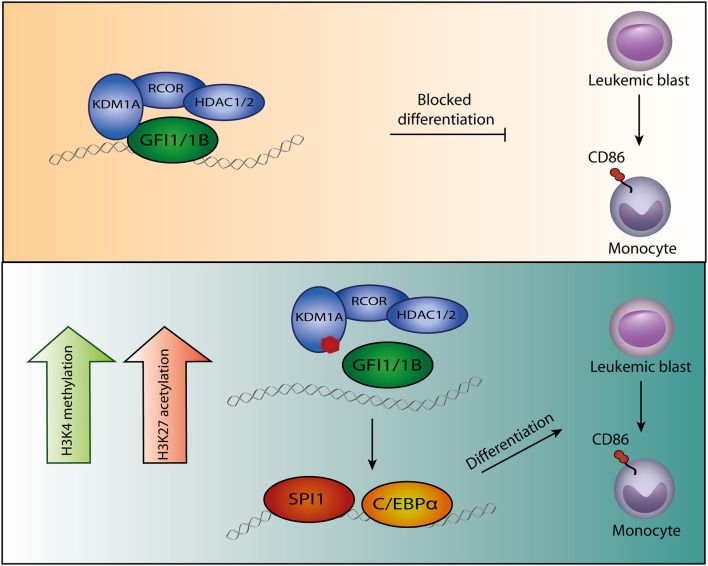
Figure 1.
Model of GFI1/1B-KDM1A inhibition. By interacting with transcription factors GFI1/1B, the CoREST complex is recruited to DNA. (Upper panel) The CoREST complex catalyzes demethylation of histone marks H3K4me1/H3K4me2 and H3K9me1/H3K9me2, resulting in chromatin modifications and altered gene expression. The complex is stabilized by RCOR, which also facilitates HDAC1/2 binding. The HDACs contribute to gene repression by H3K9ac and H3K27ac deacetylation. In acute myeloid leukemia cells, GFI1/1B-CoREST contribute to a block in monocytic differentiation. (Lower panel) Small molecules (indicated by the red polygon) bind to FAD and inhibit the function of KDM1A as well as the interaction with transcription factors GFI1/1B. The release of GFI1-CoREST from chromatin allows binding of the myeloid transcription factors SPI1 and C/EBPα resulting in gene expression that forces the malignant cells to differentiate toward monocytes, exemplified by CD86 expression.