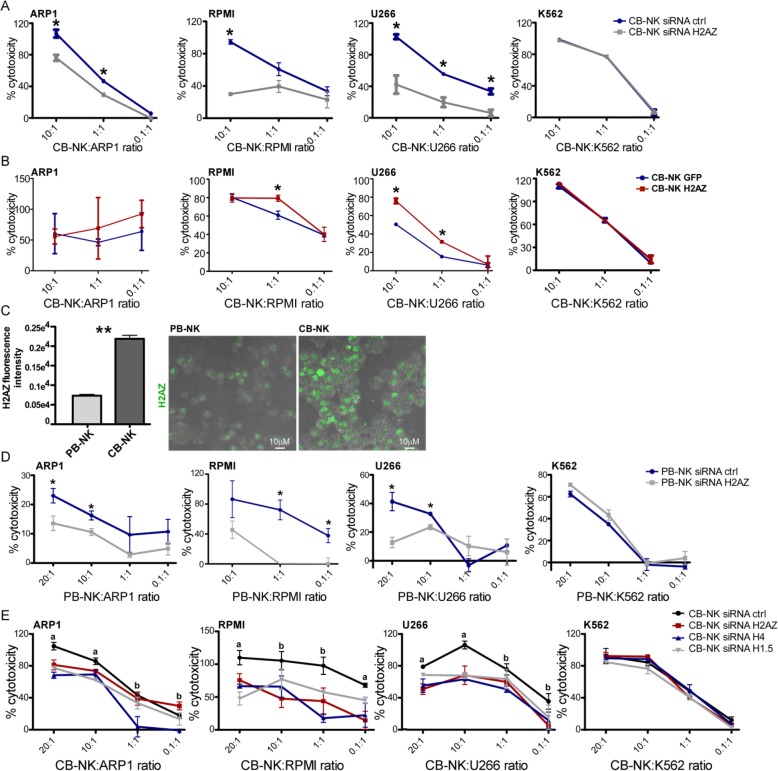
Fig. 3.
Histones are involved in CB-NK anti-MM activity. a. 3 h cytotoxicity assays comparing CB-NK control (CB-NK siRNA ctrl) vs CB-NK with knockdown of H2AZ (CB-NK siRNA H2AZ). b. 3 h cytotoxicity assays comparing CB-NK control (CB-NK GFP) vs CB-NK over-expressing H2AZ (CB-NK H2AZ). c. H2AZ levels in peripheral blood NK cells (PB-NK) vs CB-NK, analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Representative image of H2AZ levels is shown on the right. d. 3 h cytotoxicity assays comparing PB-NK control (PB-NK siRNA ctrl) vs PB-NK with knockdown of H2AZ (PB-NK siRNA H2AZ). e. 3 h cytotoxicity assays comparing CB-NK (CB-NK siRNA ctrl) with CB-NK where histones H2AZ, H4 and H1.5 were knockdown. Assays were performed at least in three independent experiments. a: all groups analyzed compared to CB-NK siRNA ctrl are different (p < 0.05). b: at least one group analyzed compared to CB-NK siRNA ctrl is different (p < 0.05). *p < 0.05. ** p < 0.001. Efficiency of knockdown of H2AZ was confirmed by Western Blot and by flow cytometry (Additional file 1: Figure S3)