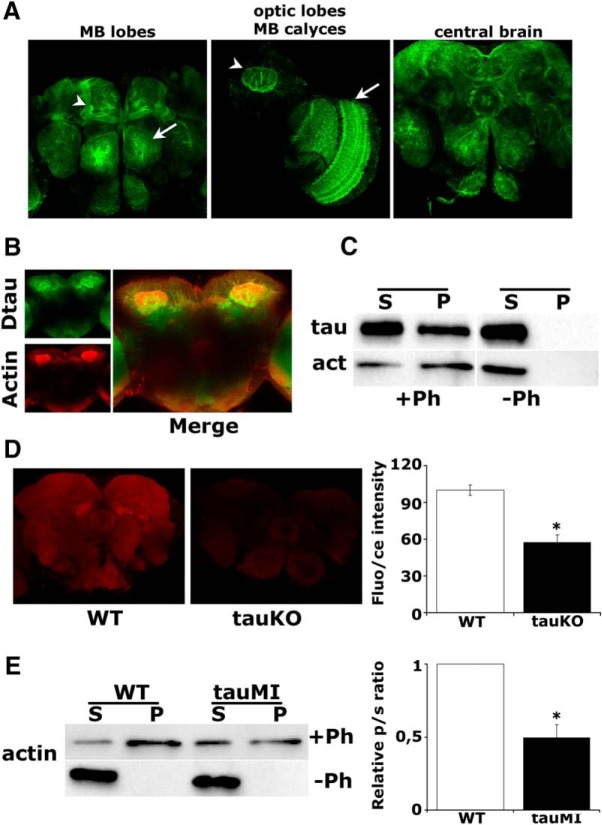
Figure 2.
dTau loss affects the actin cytoskeleton. A, Expression pattern of a GFP::dTau protein-trap in the adult brain at the level of the MB lobes (arrowhead) and antennal lobe (arrow; left), MB calyx (arrowhead) and optic lobe (arrow), (middle), and the central brain (right). B, Prominent colocalization of rhodamine-phalloidin-stained F-actin with the GFP::dTau fusion protein in adult MBs. C, Coprecipitation of phalloidin-bound F-actin and dTau from WT fly brains. D, Confocal images in the central fly brain following rhodamine-phalloidin staining of whole-mount brains from WT and tauKO flies (arrow, ellipsoid body). The mean relative fluorescence intensities ± SEM are shown as a percentage of control. E, Phalloidin-bound F-actin was isolated from fresh brain extracts of WT and tauMI mutants, and its levels were assessed by probing for actin. The ratio of precipitated actin in the pellet (p) to the actin in the supernatant (s) was used for quantification and was significantly different in the mutant, as indicated by the star.