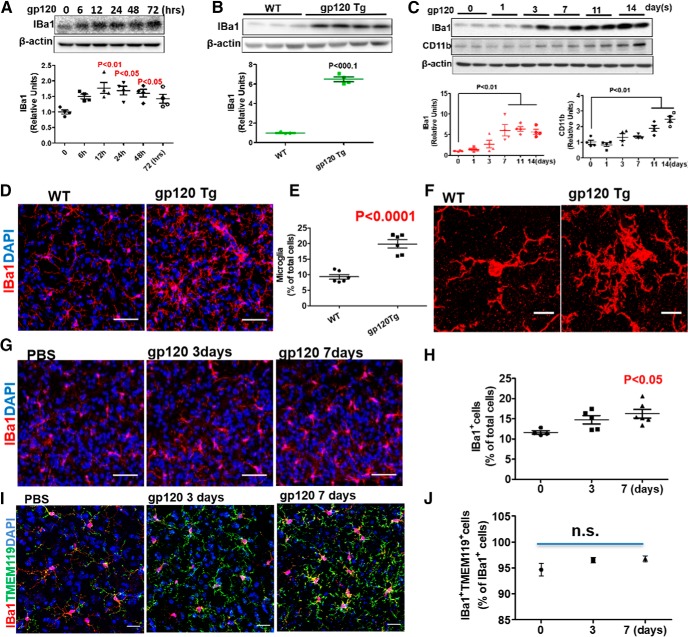
Figure 3.
Gp120 causes microglial activation. A, Levels of IBa1 in 200 pm gp120-treated primary cortical cultures (N = 4 cultures in each condition). The cell composition of the cocultures is shown in Figure 3-1. B, IBa1 in L4–L5 spinal cords from gp120 transgenic and WT mice. WT, N = 3 mice; gp120 Tg, N = 4 mice. C, IBa1 and CD11b in L4–L5 spinal cords from mice after intrathecal gp120 injection (500 ng/injection). N = 4 mice/time point. D, Confocal images of IBa1+ cells in the SDH from WT and gp120 Tg mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. E, Quantitative summary of D (mean ± SEM); N = 6 mice/group. F, High-magnification images showing morphological characteristics of reactive microglia. Scale bars, 10 μm. G, Confocal images of IBa1+ cells in the SDH of mice intrathecally injected with PBS or gp120. Scale bars, 50 μm. H, Quantitative summary of G (mean ± SEM); PBS, N = 4 mice; gp120/3 d, N = 5 mice; gp120/7 d, N = 6 mice. I, Confocal images of IBa1 and TMEM119 double-positive cells in the SDH of mice intrathecally injected with PBS or gp120. Scale bars, 30 μm. J, Quantitative summary of I (mean ± SEM); PBS, N = 4 mice; gp120/3 d; N = 5 mice; gp120/7 d, N = 6 mice. n.s., no significant difference.