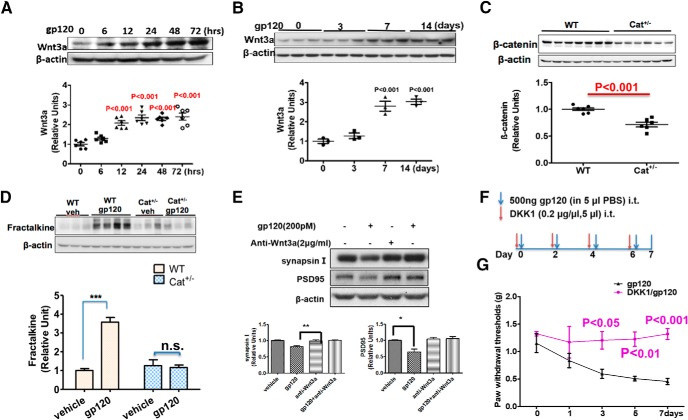
Figure 6.
Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway mediates gp120-induced FKN upregulation and synaptic degeneration. A, Temporal profiles of Wnt3a expression in gp120-treated primary cortical cultures (N = 6 cultures/group). B, Temporal profiles of Wnt3a expression in the spinal cords (L4–L5) from mice after intrathecal injection with gp120 (N = 3 mice/group). C, β-catenin protein level in spinal cords (L4–L5) from WT and Cat+/− mice (N = 6 mice for WT; and N = 7 mice for Cat+/−). D, Comparison of the effect of gp120 on FKN expression in WT and Cat+/− mice, with intrathecal injection with gp120 every other day for 7 d. Spinal (L4–L5) FKN protein was analyzed by Western blotting. N = 3 mice/group for Veh/WT, Veh/Cat+/−, and gp120/Cat+/−; N = 4 mice for gp120/WT. E, Effect of Wnt3a neutralizing antibody on gp120-induced synaptic degeneration in primary cortical cultures. Anti-Wnt3a antibody (2 μg/ml) was added to the cultures for 30 min, and then gp120 (200pΜ) was added for an additional 12 h (N = 3 independent cultures/group). F, Drug administration paradigm. DKK1 (1 μg/5 μl) was injected 30 min before gp120 (500 ng/5 μl, i.t., in PBS) injection. G, Behavioral tests of the effect of DKK1 on gp120-induced mechanical allodynia. The threshold of mechanical sensitivity in the hindpaw was measured by von Frey tests (N = 6 mice/group). Error bars indicated the mean ± SEM. n.s., no significant difference, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.