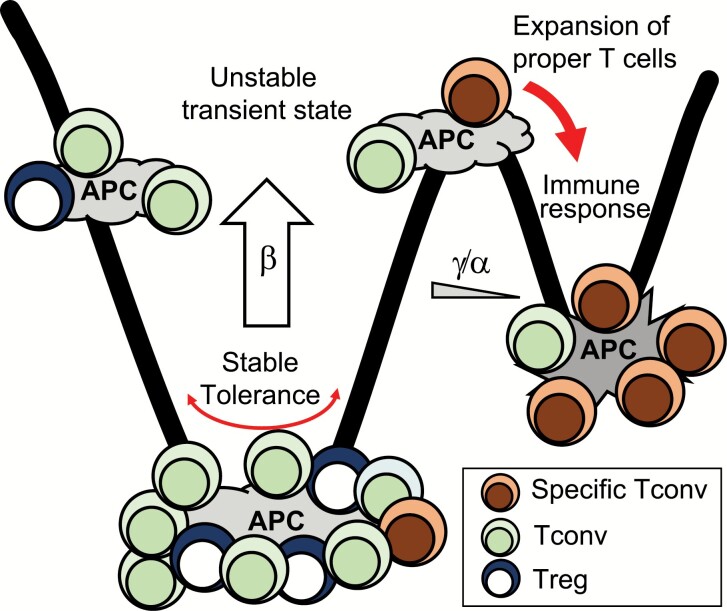
Fig. 8.
A regulation model of the immune system. Tregs on APCs increase heterogeneous T cells interacting with APCs by reducing the dissociation probability (β) and by increasing the ratio of new association to amplification (γ/α). When infected, the lack of reactive Tregs reduces the number of T cells on APCs by increasing dissociation probability. The low number of T cells on APCs induces high deviation of the fraction. While APCs with Tregs return to the tolerant state, some APCs are dominated by Tconvs because of the stochasticity. On the APC dominated by Tconvs, specific Tconvs with high affinity amplify the interaction and preferentially proliferate inevitably.