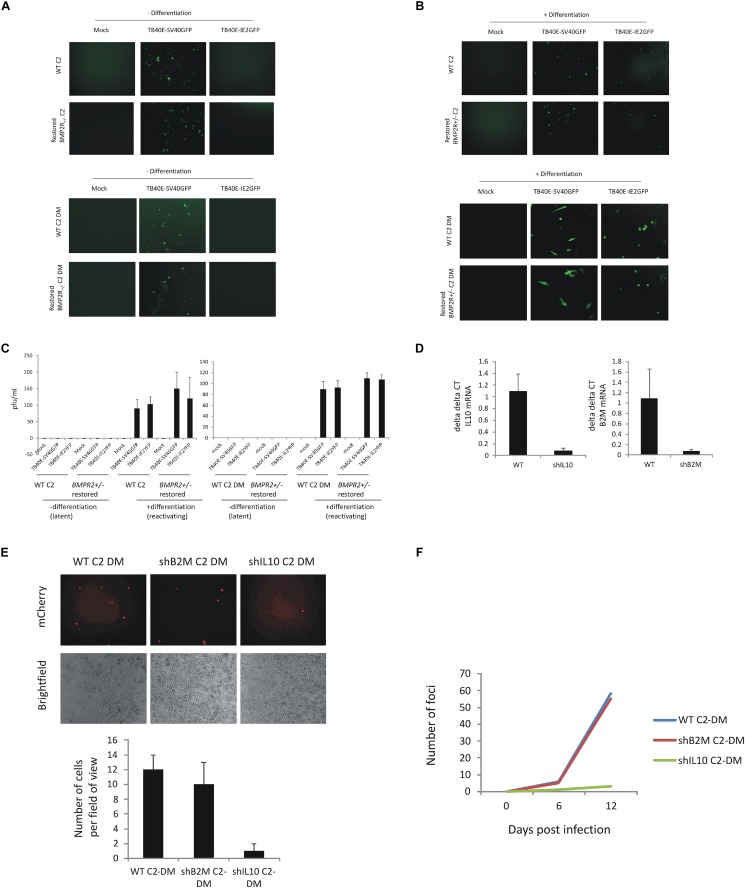
FIGURE 3.
C2 iPSCs retain the ability to support HCMV latency and reactivate virus after CRISPR/Cas9 editing and removal of cellular IL10 by lentiviral shRNA decreases HCMV maintenance and reactivation. C2 iPSCs or C2 iPSCs which have been mutated using CRISP-R directed gene editing (BMPR2 ± C2 iPSCs or derived monocytes) were restored for WT BMP2 levels using 50 ng/ml BMP4 (BioTechne) before infecting with either TB40E-SV40GFP (MOI 5) or TB40E-IE2YFP (MOI 5) and during which time latency is supported for 4 days (A) before differentiating to induce reactivation (B). Supernatants were collected and virion production was assessed by transferring to fibroblasts (C). C2 iPSCs were also lentivirally transduced with lentiviral vectors delivering shIL10 or shB2M to cells. Following establishment of the C2 shIL10 and B2M knockout cell line, cells were differentiated into C2 DMs and validated by RTqPCR alongside WT C2 DMs (D). WT C2 DM, B2M C2 DM, and shIL10 C2 DM cells were then latently infected with TB40E-GATA2-mCherry strain of HCMV (MOI 5) and analyzed by immunofluorescence 6 days later for the presence of the mCherry marker and fields of view were enumerated (E). The release of virus was assessed following differentiation of the C2 DMs into C2 DCs and analyzing the formation of foci of infection with fibroblasts (F).