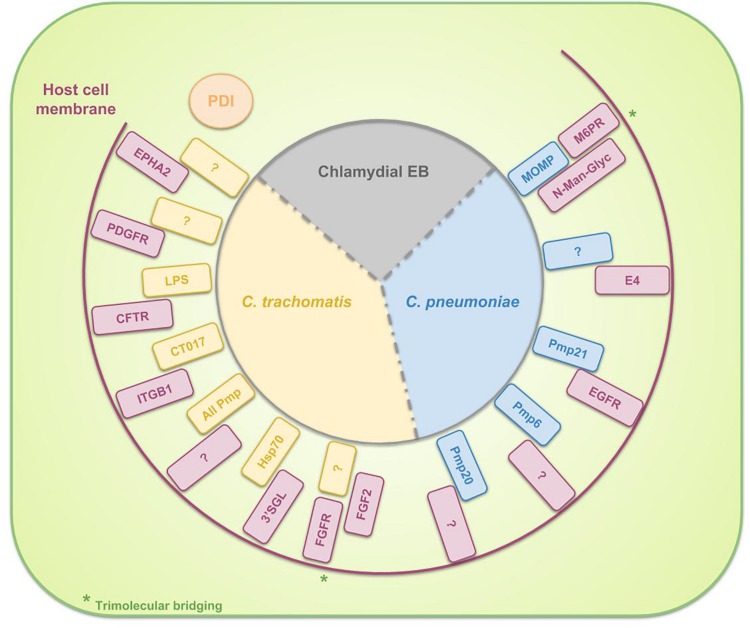
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of the binding partners, involved in the binding of EBs to the surface of host cells. For C. trachomatis three complete binding partners are identified: chlamydial LPS and host Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR), chlamydial CT017 and host beta-1 integrin (ITGB1) and chlamydial heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) and host 3′sulfogalactolipid (3′SGL). Furthermore, several chlamydial adhesins or host receptors are known to be involved in the attachment of C. trachomatis EBs to the host cell without knowing their binding partners: host Ephrin receptor A2 (EPHA2), Platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) and Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) (by means of Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) bridging) and all chlamydial polymorphic membrane proteins (Pmps). For C. pneumoniae the identified binding couples to date are chlamydial Pmp21 and host Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and chlamydial MOMP and host mannose 6-phosphate receptor (M6PR) (by means of N-Man-Glyc bridging). Host PDI is necessary for EB attachment to the cell but the bacterium does not bind directly to the PDI. Instead, Chlamydia attaches to a host protein, associated with PDI.