Figure 1.
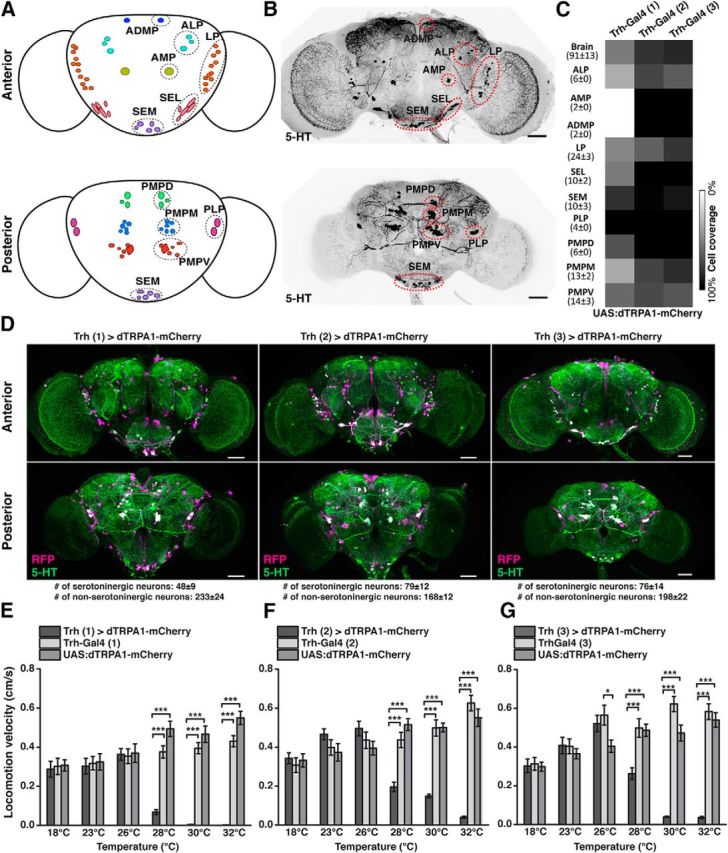
Thermogenetic activation of Trh-Gal4-positive neurons induces behavioral quiescence. A, Schematic illustration of 5-HT neuron clusters in the central brain. B, 5-HT-immunoreactive neurons in the brain. C, Coverage of 5-HT neurons by three different Trh-Gal4 strains. Numbers in parentheses indicate the total numbers of 5-HT-immunoreactive neurons for each cluster in both central brain hemispheres (mean ± SD, n = 18). Grayscale represents the relative coverage of these neurons by the three Trh-Gal4 lines when UAS:dTRPA1-mCherry is used as a reporter (n = 3 brains each). D, Expression of dTRPA1-mCherry under control of the three Trh-Gal4 lines. Magenta represents anti-RFP immunostaining against dTRPA1-mCherry. Green represents anti-5-HT immunostaining. White represents the overlap. Images represent maximal intensity z-axis projections across stacks of confocal images. The numbers of somata are indicated below the panels (mean ± SD, n = 3 brains). E–G, Temperature-dependent decrease in locomotion velocity in flies expressing dTRPA1-mCherry under control of the three Trh-Gal4 lines compared with the heterozygous Trh-Gal4 lines and the heterozygous UAS:dTRPA1-mCherry line. Bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 27 each). *p < 0.05. ***p < 0.001. For exact statistical values, see Table 3. Scale bars, 50 μm.
