Figure 8.
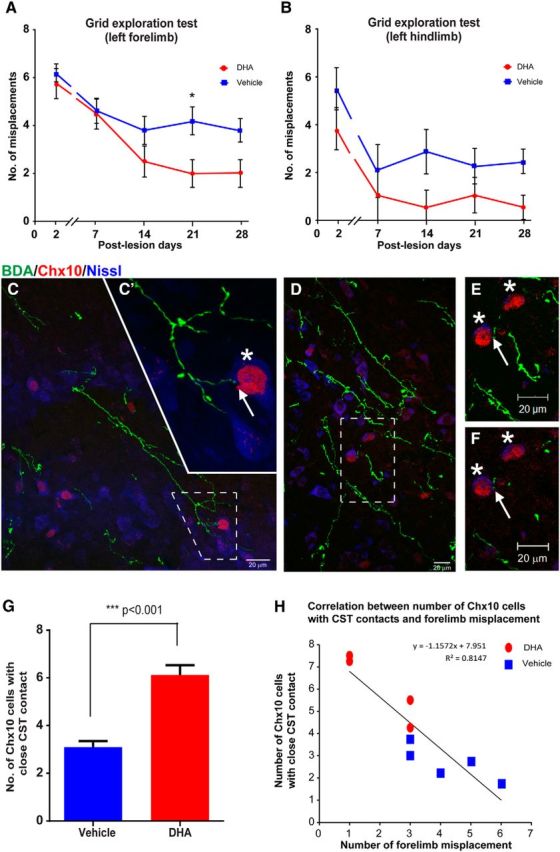
DHA enhances functional recovery via connection with Chx10 interneurons in pyramidotomy mice. A, Mice with a unilateral pyramidotomy failed to initially accurately place the left forepaw (requiring integrity of the lesioned CST) onto the grid after injury, but the DHA-treated rats (red circles) made significantly fewer misplacements at 3 weeks after injury compared with vehicle-treated mice (blue squares). B, The analysis revealed that DHA-treated mice (red circles) made fewer errors with their left hindpaw, but not significantly less than vehicle group animals (blue squares) throughout the testing period. C–F, Confocal images of mouse cervical spinal cord transverse sections at the intermediate laminae of the CST-denervated side showing examples of BDA-labeled CST collaterals (green) in the vicinity of blue fluorescent Nissl-stained cells (Neurotrace 435/455), some of which are V2a interneurons identified by immunostaining for Chx10 (red). C, D, Dashed boxes represent high magnification in C′, and in E, F, which reveal contacts (arrows) between BDA-labeled collaterals and Chx10 interneurons (asterisks). C′, A Z-stack comprising 10× 0.66 μm optical images. E, A Z-stack comprising 25 × 0.72 μm optical images. F, A single 0.72 μm optical image. Examination of the single optical image confirms that the BDA-labeled CST fiber contacts (arrow) one of the Chx10 interneurons. G, Quantitative analysis revealed a significant increase in the number of Chx10 interneurons contacted by BDA-labeled CST collaterals following DHA treatment (red bar) compared with vehicle treatment (blue bar). H, A strong negative correlation was observed between the numbers of Chx10 interneurons with BDA-labeled CST contacts and the numbers of forelimb misplacements. Data were taken from DHA-treated (red circle) and vehicle-treated (blue square) animals. ***p < 0.001, DHA versus vehicle group. Scale bar, 20 μm.
