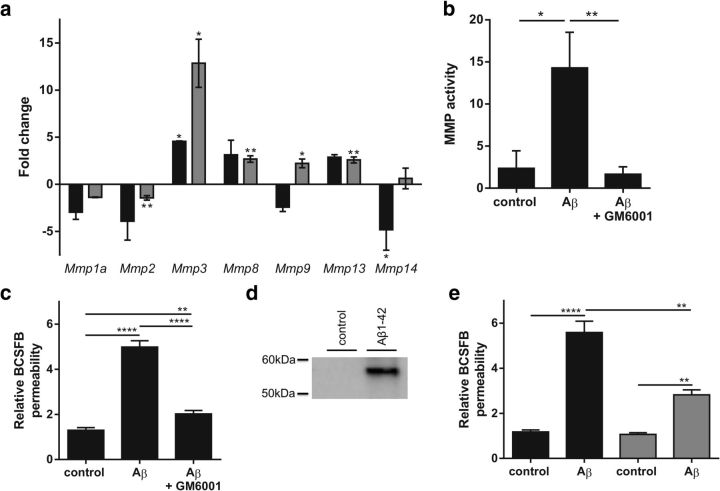
Figure 6.
Analysis of the role of MMPs in Aβ1–42 oligomer-induced disruption of BCSFB permeability. a, Fold change in Mmp gene expression in the CP 2 h (black) and 6 h (gray) after intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ1–42 oligomers in the cerebral ventricles compared with control samples (n = 3–4). b, Total MMP activity in CSF of C57BL/6 mice 6 h after intracerebroventricular injection of scrambled peptide (control), Aβ1–42 oligomers (Aβ), or Aβ1–42 oligomers together with GM6001 (Aβ + GM6001) (n = 6). c, BCSFB permeability of C57BL/6 mice 6 h after intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ1–42 oligomers alone (Aβ) or combined with the MMP inhibitor GM6001 (Aβ + GM6001) compared with scrambled peptide injected mice (control) (n = 6–7). d, Western blot analysis of MMP3 protein levels in CSF of control and Aβ1–42 oligomer intracerebroventricularly injected mice. e, Relative BCSFB permeability in wild-type (black) and MMP3−/− (gray) C57BL/6 mice 6 h after intracerebroventricular injection of scrambled control or Aβ1–42 oligomers (n = 4–10).