Figure 7.
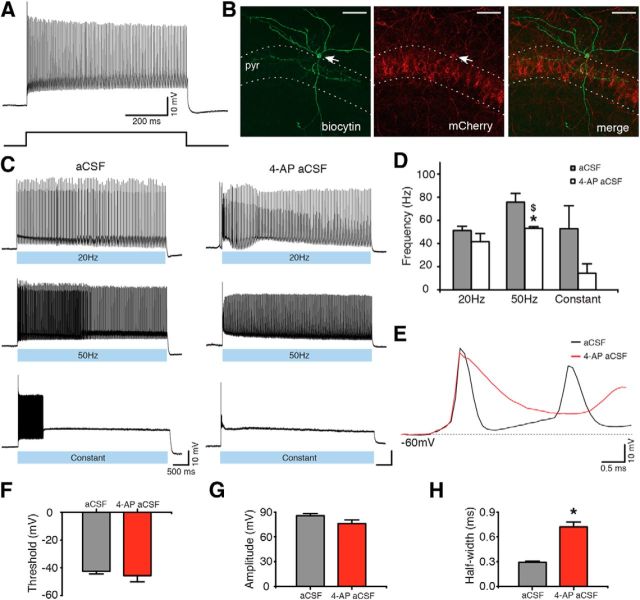
ChR2-expressing PV interneurons generate APs upon blue light illumination. A, Whole-cell recording (top) of a PV interneuron generating typical high-frequency nonaccommodating APs upon sustained 500 pA current injection (bottom). B, Confocal image showing biocytin (left) and mCherry (middle) staining of the PV interneuron shown in A. Merged image is shown on the right. Scale bars, 50 μm. pyr, Stratum pyramidale. C, Whole-cell recordings from the cell shown in A and B illustrating APs during 20 Hz, 50 Hz, or constant blue light illumination for 5 s, in aCSF (left) and in 4-AP aCSF (right). D, Bar chart of averaged data from experiments shown in C (n = 5 in normal aCSF and n = 6 in 4-AP aCSF). *Statistically significant difference between the AP frequency in aCSF and 4-AP aCSF: paired t test (p = 0.030). $Significant difference between the firing frequency during 50 Hz versus constant light illumination paradigms in 4-AP aCSF: Kruskal–Wallis test (p = 0.003), Dunn's multiple-comparison test (p < 0.05). E, The first AP induced by 20 Hz blue light illumination in aCSF (black) and in 4-AP aCSF (red). F–H, Average characteristics of the first APs induced by 20 Hz blue light illumination in the presence of aCSF (gray bar, n = 5) or 4-AP aCSF (red bar, n = 5). *Statistically significant difference between the two experimental conditions: paired t test. F, Average AP threshold (p = 0.105). G, Average AP amplitude (p = 0.444). H, Average AP half-width (p = 0.001). Values represent mean ± SEM.