Figure 4.
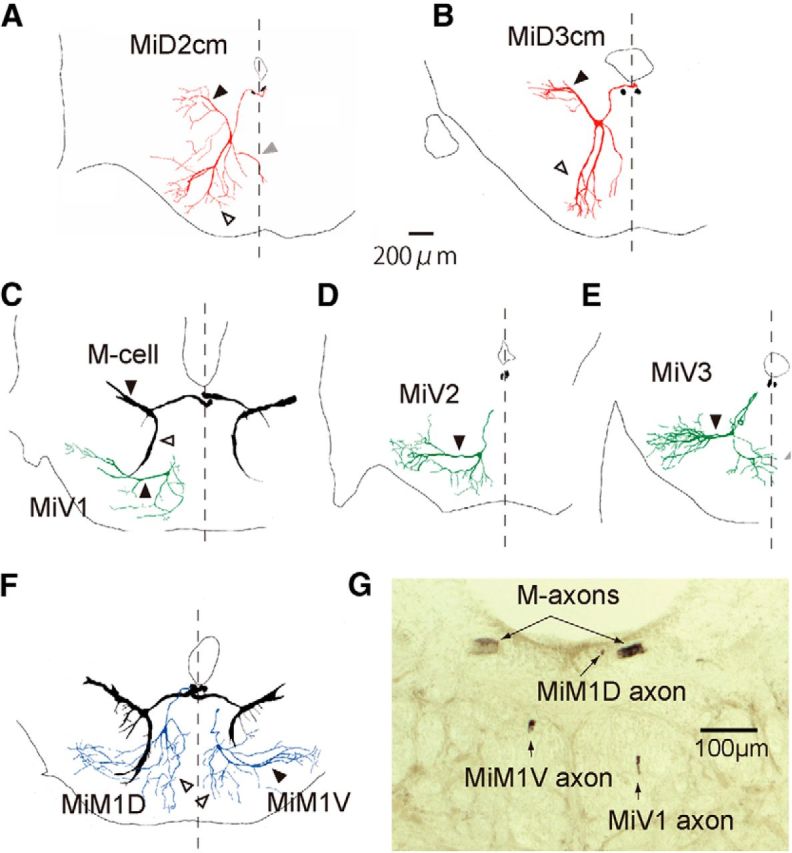
Frontally stacked images of reticulospinal neurons in r4–r6 with the Mauthner cell. Camera lucida reconstructions of rostral view from serial frontal sections of intracellularly labeled the M-cells (black) and other RSNs in r4–r6. A, B, The right MiD2cm cell in r5 (A) and MiD3cm cell in r6 (B) had an axon that dorsally projected to the dorsal bundle of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (mlfd), where the M-axon extended. Sections of bilateral M-axons are shown in black. MiD2cm cells in r5 had a medial dendrite (gray arrowheads) that extended to the midline (broken lines). C–E, Ventrally located MiV1 cell in r4 (C), MiV2 cell in r5 (D), and MiV3 cell in r6 (E) had an axon projecting to the ventral bundle of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (mlfv), which was located ventral to the M-axon. F, Simultaneous labeling of MiM1D (left) and MiM1V (right) cells with bilateral M-cells revealed the morphological differences of dendrites: the MiM1D cell possesses ventrally projecting bifurcated dendrites (open arrowhead), whereas the MiM1V cell possesses a thick lateral dendrite (filled arrowhead). Dorsal is up. The calibration in A is also applicable to B–F. G, A micrograph of the frontal section at the level of the caudal hindbrain. The MiM1D axon extended along with M-axons in the mlfd, whereas MiM1V and MiV1 axons were located in dorsal and ventral mlfv, respectively.
