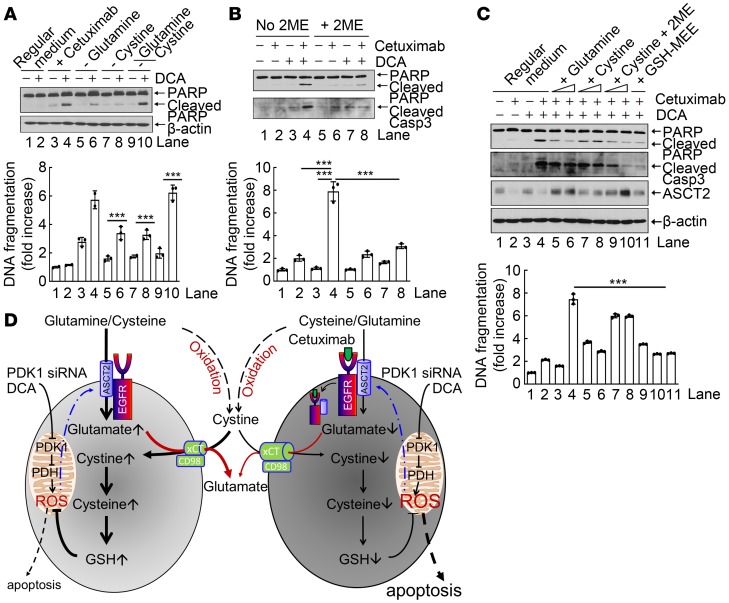
Figure 5. Cetuximab sensitizes HNSCC cells to DCA-induced apoptosis via diminishing ASCT2-mediated glutamine uptake.
(A–C) HN5 cells were treated as indicated, and cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (upper panels) and to ELISA for quantification of apoptosis (lower panels). (A) The cells were cultured in regular medium or glutamine- and/or cystine-deficient medium with or without 10 mM DCA for 24 hours. (B) The cells were left untreated or treated with cetuximab, DCA, or both as indicated for 24 hours in medium with or without addition of 10 μM 2-mercaptoethanol (2ME). (C) The cells were left untreated or treated with cetuximab, DCA, or both as indicated for 24 hours in regular medium; regular medium supplemented with additional glutamine (final concentrations 5 mM and 10 mM in lanes 5 and 6, respectively) or cystine (final concentrations 0.2 mM and 0.4 mM in lanes 7 and 8 or final concentrations 0.2 mM and 0.4 mM plus 10 μM 2ME in lanes 9 and 10, respectively); or regular medium supplemented with 10 mM glutathione monoethyl ester (GSH-MEE). All error bars indicate ± SD. ***P < 0.001 (2-way ANOVA, n = 3). (D) Proposed working model in which cetuximab diminishes intracellular glutathione via downregulation of the ASCT2-EGFR complex, thereby sensitizing cells to PDK siRNA– or DCA-induced apoptosis.