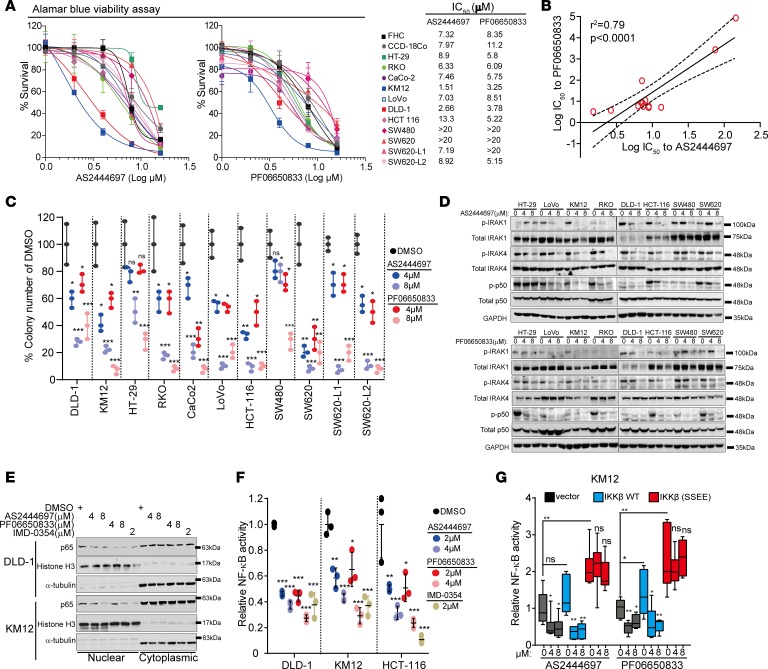
Figure 5. IRAK4 inhibitors suppress NF-κB activity in CRC cells.
(A) Alamar Blue assay showing the viability of colon cancer lines cultured in serial concentrations of 2 different IRAK4 inhibitors for 5 days, and the respective IC50 values. Data represent 1 of 3 sets of experiments each done in triplicate. (B) Correlative analyses of IC50 values between the 2 indicated IRAK4 inhibitors in colon cancer cell lines. (C) Quantification of clones formed by the indicated CRC lines treated with DMSO or 2 different IRAK4 inhibitors over 3 weeks. Data represent 1 of 3 sets of experiments each done in triplicate and presented as mean ± SEM (ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (D) Western blots showing the suppressive effect of 2 different IRAK4 inhibitors on the indicated markers after overnight treatment. (E) Western blots showing diminished abundance of nuclear p65 in 2 different CRC cell lines treated with both IRAK4 inhibitors overnight. The IKKβ inhibitor IMD-0354 served as positive control. (F) NF-κB luciferase reporter assay of different CRC lines incubated with DMSO or the indicated inhibitors overnight. Data represent 1 of 3 sets of experiments each done in triplicate and presented as mean ± SEM (ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (G) NF-κB luciferase reporter assay of KM12 cells transfected with empty vector, WT, or constitutively activated (S177E/S181E) IKKβ incubated with DMSO or the indicated IRAK4 inhibitors overnight. Data represent 1 of 3 sets of experiments each done in triplicate and presented as mean ± SEM (Tukey’s multiple-comparisons test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).